DevSecOps Cloud Security Solutions Buyer’s Guide
The cloud has come a long way from Eric Schmidt’s “modern” coining of the phrase in 2006. Today, companies and institutions are reliant upon a cloud infrastructure to run their day-to-day operations.
This reliance and growth have also transformed the threat landscape and your cybersecurity requirements along with it. Though cloud service providers are working ceaselessly to shore up vulnerabilities and bolster defenses, the responsibility for your cloud assets does not solely lie with them. Estimates predict that by 2025, 99% of cloud failures will be caused by the customer.
Recent news headlines like the SolarWinds breach illuminate the potential fallout of this gap in securing customer cloud base services and applications. A broad array of solutions to choose from, each with its own feature set, complicates the process further. Trying to distinguish between them can be daunting, which is where this buyer’s guide comes in.
Our guide will dive into the hurdles of securing your cloud infrastructure and the opportunities present in streamlining your cloud security stack. We will explain the primary features of these cloud security solutions and how to select the right tool or tools to secure your organization’s cloud applications. We will propose examples of several leading cloud security solutions to help narrow down your search before you even begin.
DevOps Challenges In The Cloud
Current software development relies on cloud services and APIs to increase productivity, information flow, and reliability throughout the CI/CD pipeline. Services such as Slack for interpersonal business communication and collaboration, GitHub for code management, or Amazon AWS and Google APIs for almost anything you can think of, from geolocation translations to on-demand server instancing.
According to GitHub’s 2021 Global DevSecOps Survey, 60% of developers release code twice as fast thanks to DevOps, while 72% of security professionals rated their security efforts as “good” or “strong” due to the expanded use of SAST and DAST technologies.
As cloud solutions are becoming the standard and cloud spending is rising, cyber hackers have realized that new technologies can present new exploitable vulnerabilities. Inadequate credential management, secret leaks, misconfigurations, data breaches, lax security practices, account hijacking, and human error are just a few of the growing threats to cloud infrastructure.
Shifts in cyber-crime push cloud technology to the center of almost every cyber attack. Considering that nearly all organizations suffered at least one data breach in the past 18 months, the worry is warranted.
These figures align with a recent survey that found that 92% of security leaders report moderate to significant security gaps due to fast-paced cloud migration outpacing cloud security adoption. A lack of clear migration strategies and a tendency of organizations to perform a complete transfer to the cloud all at once make the situation worse.
The COVID pandemic hasn’t done cloud cybersecurity any favors either. From January to April 2020, attacks against PaaS and IaaS cloud assets exploded by 630%, and cyberattacks against native cloud infrastructure and containers jumped 250% to over 16,000 incidents in the last year alone.
The steep rise in attacks against cloud assets and infrastructure makes it even more crucial not to underestimate the potential cost of a cyber attack. An outage to a single large cloud service provider like AWS or Azure lasting for 3-6 days has a cost estimate that could exceed $15 billion.
While the outcomes of a cyber offense are pretty severe, they are also relatively straightforward. The conditions that enable them are diverse. However, significant obstacles remain on the path to smooth, secure cloud migration.
Rising multi-cloud use across dev teams and projects
Each development team and project uses cloud infrastructure and SaaS apps in particular ways, and these don’t always line up across various users, departments, and interfaces. Each tool has its unique security controls and requirements, making it difficult to manage access across the entire company.
This phenomenon has become so widespread that they have given it its own term – “multi-cloud architecture.” 92% of enterprises reported adopting a multi-cloud strategy to meet their cloud environment needs in 2020. This statistic lines up with a reported average of 2.6 public and 2.7 private clouds deployed per organization.
The same is true for SaaS applications. Depending on its size, the average organization uses between 102 and 288 SaaS apps simultaneously, and the average employee relies on at least 8. As more teams within your company turn to cloud services and apps, managing their secure usage becomes increasingly convoluted.
Unclear shared responsibility
In theory, cloud security is a delineated, collaborative endeavor between cloud users and service providers.
However, the shared responsibility model is rarely so straightforward. There are specific inherent responsibilities between the service provider and users. Nevertheless, most applications and services between those clear divisions fall into a vast gray area of unknown responsibility.

Stressing the issue is a stark discrepancy between actual duties and what customers and cloud service providers perceive as a shared responsibility. More than half, and sometimes, almost two-thirds of these individuals erroneously believed the burden was on the other party.
Long resolution processes
The average business can save $1 million if they resolve a breach within the first 30 days.
Unfortunately, the average time to contain a breach was a worrying 80 days. Even more concerning is the fact it takes an average of 228 days just to detect the breach. From detection to resolution, that means the average breach takes nearly a year to conclude, a period that, for most organizations, would spell disaster.
The complexity of the ecosystem and number of product categories
The cloud ecosystem is becoming increasingly convoluted, and cloud security is along with it. On average, organizations use an average of 100 unique security controls. So it’s no wonder that 70% of security specialists in these organizations believe there are far too many specialized security tools available and required to secure their cloud ecosystem. There are also a variety of product categories and subcategories that further obfuscate the situation.
Another thorn in the side of adequate cloud security is that each cloud provider uses its own convoluted and proprietary platform. Which, though architecturally rich, creates chaos. This chaos is due to each platform requiring its unique security controls and securing cloud assets requiring a novel approach and expertise for each. Last, there is a disconnect between users like developers creating new cloud accounts and workloads, and DevSecOps personnel, struggling to secure their cloud stack.
Now that the challenges to establishing a solid cloud security strategy have are clear, a baseline understanding of what these solutions can do in practice is necessary.
Critical Roles Of Cloud Security Solutions
Identification & visibility
One of the most challenging aspects of securing business cloud operations and applications is the many architectures, configurations, applications, and services relied upon by different teams within an organization. This variety creates a massive headache in terms of visibility. To complicate things further, individuals with little experience in cloud security often make purchasing decisions.
Cloud security solutions offer a centralized hub that presents clear security policies, access controls, cloud configurations, and usage across your cloud ecosystem. Having a scripted tool crawling your cloud ecosystem leaves little room for error, vulnerability, or even breach from escaping your notice.
It is especially relevant for cloud monitoring, as most companies rely on third-party cloud services that don’t have complete access and control over the organization’s cloud stack.
Monitoring
Active monitoring of your organization’s cloud ecosystem is one of the preeminent elements of a successful cloud security stack. The reliability of service providers in delivering real-time threat assessments and vulnerability discovery has also subsequently increased. This includes measuring and analyzing cloud behavior in terms of data, applications, and infrastructure.
Through monitoring, cloud security solutions have become instrumental in proactively detecting and remediating vulnerabilities and malicious behavior within your cloud network. This promise of intelligent threat detection is one of the driving forces behind increasing cloud adoption and the migration of enterprise and business activities to remote cloud services.
Cloud security tools are not solely limited to preventing maleficence. They can identify areas where your workload and workflow can be optimized and analyze resource usage and allocation to detect potential future vulnerabilities and issues.
Resolution streamlining
Cloud security solutions aim to optimize and quicken response times faster than most human DevSecOps professionals can react manually. A well-rounded cloud security solution will provide these services from detection to alert, remediation, and analysis.
You should also expect a clear and comprehensive Service-Level Agreement with any security service provider you choose in terms of mitigation time and quality of resolution. An SLA based only on response time helps little when you have an incident, and a quick response still leaves your cloud operations crippled.
Operational benefits
The ever-shifting cloud environment causes various miscommunications and breakdowns in the chain of operations between departments. Cloud security solutions aim to protect your cloud ecosystem faster, easier, and overall cheaper. The time saved by tasking DevSecOps staff to actively protect cloud resources, each with its expertise required, cannot be understated.
Also, as previously mentioned, there is a significant issue with a lack of qualified staff to manage and secure cloud environments properly. These solutions remove a great deal of the pressure on management to find suitable personnel to fill the gap. This also extends to internal efforts within your organization to improve interdepartmental communication and coordination. Last, these tools are a proactive and intelligent method for testing and maintaining compliance and implementing consistent security policies for all cloud usage.
What To Look For When Choosing Cloud Security Solutions
Scalability
As we’ve mentioned several times, cloud adoption and usage are rapidly increasing, which means solutions to secure these growing ecosystems need to scale with them. The trouble is determining what level scale is sufficient, as many vendors offer protection from any DDoS or similar attack regardless of the size. Yet, in reality, this is not always the case. Your organization needs to dive into any security solution’s stated maximum capacity to ensure that when you need it, your security solution can protect you from the most multi-vector, large-scale attacks and breaches.
Flexibility
Cloud usage and migration are growing, and organizations’ needs are pivoting and changing all the time. Cloud security tools need to be just as fluid and adapt to new platforms and technologies as they are introduced to the ecosystem. This also includes maintaining stability, regardless of sudden spikes in traffic, legitimate or malicious. A proper cloud security solution will provide your organization with the flexibility to avoid server disruptions and unnecessary downtime while optimizing lower-volume periods to lower costs.
Automation
The best kind of security is the one you never see but is working in the background silently. Any cloud security solution worth your time will help to significantly free up your DevSecOps resources and personnel while streamlining security controls. The incident response must activate within minutes or even seconds to mitigate the potential attack vector, which is prone to human error. For this reason, automated scripts running as part of the security solution should be a significant deciding factor.
Low impact on operations
Excessive cloud sprawl already takes its toll on efficient operations, so your choice in security solution must arrive with minimal impact. Your cloud security tools should also assist with testing for and remaining compliant with various security standards and protocols. That includes resolving non-compliance and other potential risks with little to no downtime.
Evolution
Cloud computing, and cloud security, are evolving at a breakneck pace. Buzzwords and tool types that are fresh and shiny one day can be rendered obsolete shortly after. Your choice in cloud security tools should reflect these rapid shifts with a solution that is consistently and quickly innovating and adapting to whatever changes arise.
Cloud Security Tool Categories
Saying “Cloud Security tools” is about as broad as saying “Antivirus.” It is truly a wide swathe of solutions, each designed to protect and maintain various aspects of your organization’s cloud infrastructure.
Cloud security tools break down into six primary categories that fulfill a particular role in protecting cloud databases, applications, and containers:
- CASB – Cloud Access Security Broker
- SAST – Static Application Security Testing
- SASE – Secure Access Service Edge
- CSPM – Cloud Security Posture Management
- CWPP – Cloud Workload Protection Platform
- CIEM – Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management
What do all these four-letter acronyms mean? And what type of solutions do you need to keep your cloud data and services secure? Let’s break it down.
What are Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) Tools
The Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) acts as a gatekeeper between cloud users and providers as cloud resources are accessed. These solutions also manage enterprises’ migration of their existing on-campus security protocols to their cloud infrastructure. This allows organizations to plug potential security holes by extending their security controls beyond the physical premises.
This extends to the cloud infrastructure (IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS) organization-wide and creates cloud-only security controls. CASB tools are based on four base concepts:
- Data Protection
- Threat Protection
- Identity
- Visibility
Top Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) Tools
1. Cisco Systems Cloudlock
Cisco’s Systems Cloudlock provides an enterprise-oriented CASB solution to manage the safe transfer of apps, data, and users on the cloud. It has an API-based ecosystem that helps organizations with compliance and to combat data breaches.
Pros:
- Streamlined workflow
- Easy to use incident management interface
- Accurate DLP detector
- Manage any file usage or access through G Suite integration
Cons:
- No free trial is available
- Security notifications are sometimes delayed and not necessarily in real-time
2. Bitglass: Total Cloud Security
BitGlass is a fresh CASB solution that assists users in the secure management of cloud frameworks from both potential data leaks and standard and Zero-Day malware. This includes real-time app management and threat detection for both managed and unmanaged cloud apps.
Pros:
- Easy setup and implementation
- Relatively inexpensive
- Control unmanaged devices via reverse proxy
Cons:
- Added security for email can be a hassle for end-users and to implement across an organization
- Errors crop up now and then hamper the workload.
What are Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Tools?
SAST tools employ technology to analyze source code and binary executables for patterns indicative of security vulnerabilities or suspicious activity. SAST tools scan for exposed secrets and credentials such as passwords, API keys, and security tokens in source code or binaries.
Some SAST tools offer functionality like continuous monitoring for dangerous vulnerabilities in open-source libraries, a digital inventory of third-party assets used in the development environment or on a production website, analysis of third-party asset behavior to determine where data is relayed, and discovery of potential security threats relating to such behavior. Finally, SAST can be used to assure licensing compliance with open-source libraries used within your organization.
Top Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Tools
3. SpectralOps
Spectral specializes in discovering secrets, vulnerabilities, and configuration issues resulting from coding errors, lacking security practices, or human error. Spectral uses AI and Machine Learning algorithms to detect secrets and vulnerabilities with a high probability while reducing false positives.
Pros:
- AI and Machine Learning algorithms are continuously evolving to face new threats in real-time
- Smoothly integrates into the CD/CI pipeline without slowing down the development pipeline
- Monitors public Git repositories used by employees for accidental or malicious commits of company assets
- Powerful integration options (Slack, logs, and more) for increased coverage
Cons:
- Price is not listed; a demo is available.
What are Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) Tools
SASE solutions are a more in-depth and independent approach to cybersecurity for DevSecOps and cloud operations. SASE offers a layered security framework for both companies and customers, with unified functionality to offer streamlined security. It is a more recent method highlighted by high-level policy management and equally compatible for both enterprises and modern businesses.
Top Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) Tools
4. Cato Networks | Cato SASE

Cato’s SASE tool is a cloud-based security solution featuring a union of SD-WAN network security and wide-ranging support for several mobile devices, cloud applications, and other services.
The centralized hub allows DevSecOps personnel to effectively and simply manage and monitor, assign, and maintain security protocols across your organization’s cloud ecosystem. It also improves cross-team productivity and provides a hands-free automation service that ensures your dependencies and all components remain up-to-date and scalable without repeat upkeep.
Pros:
- Centralized design and policy management
- Easy administration and maintenance
Cons:
- Speed issues depending on location
- The firewall is rough and requires more deep analytics capabilities
5. Perimeter 81
Perimeter 81 offers an identity-oriented, complete SASE solution with quick setup and operation without hours of optimizing and configuration. It provides efficient management of cloud assets and a handful of security controls covering physical and digital cloud infrastructure.
Pros:
- Split tunneling and DNS filtering
- No bandwidth limits
- Easy VPN configuration cross-platform (Mac, Windows, Ubuntu)
Cons:
- No free trial
- Password management with IdPs can lack
- Lack of Google Authentication
- Speed fluctuations outside of urban areas
What are Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools?
CSPM security solutions are a reliable choice for automated cloud security management, especially for organizations reliant on IaaS and PaaS equally. They are especially relevant for any organization amid the cloud migration process, with their ability to detect instances of misconfiguration during the process and automatically adjusting where necessary.
Top Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools
6. Fugue
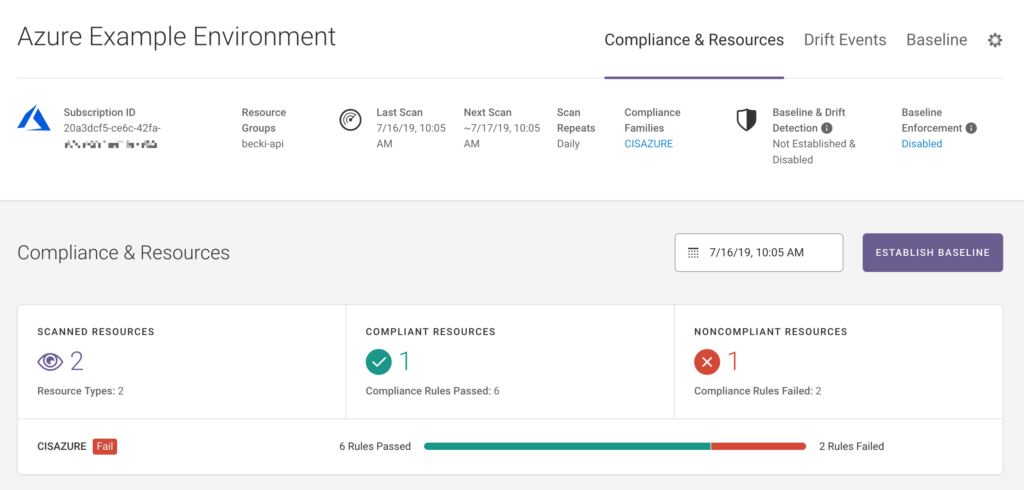
Fugue is a cloud-based enterprise-focused CSPM tool intended for engineers to offer them significantly improved visibility of their organization’s cloud security framework. It is compliance-oriented both for analysis and maintenance and provides an API for easy integration.
Pros:
- Support for multi-cloud usage
- Increased visibility and fine-grained monitoring capabilities
- Automated compliance discovery and remediation tools
Cons:
- Lack of customization focus on specific areas of cybersecurity
- Expert knowledge of cybersecurity required to draw out all of Fugues relevant cloud security features
7. XM Cyber – Attack-Centric Exposure Management
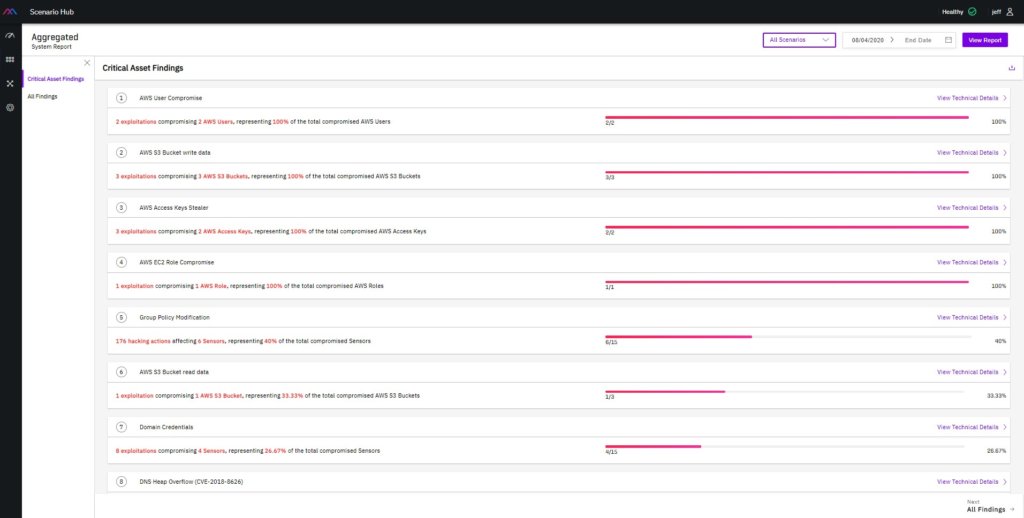
XM Cyber is a CSPM solution that focuses solely on your organization’s security management and controls. It provides users with a graphical look at their cloud network the same way that malicious actors would, offering resolution strategies based on an organization’s priorities for their cloud assets. It also includes attack simulations to discern weak points within your cloud stack.
Pros:
- Vulnerability scanning and patch management with continuous simulations and monitoring
- Battleground View for increased visibility into cloud environments
- Free Trial
Cons:
- Pricing upon request
- Hyper-focused on attack simulation to discern and fix weak points leaves several important features less present
What are Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)?
CWPP security tools are cloud workload-focused, protecting both physical and digital assets for enterprises. They provide server-side workload protection for public IaaS cloud assets, along with visibility and management for the entire cloud ecosystem, physical and virtual, from a single platform.
Because of organizations’ continuing need for legacy apps and frameworks support, a complete migration to the cloud is usually not worth the return on investment. CWPP solutions bridge the security gap for outmoded devices and those legacy apps on the cloud.
Top Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
8. Illumio Core
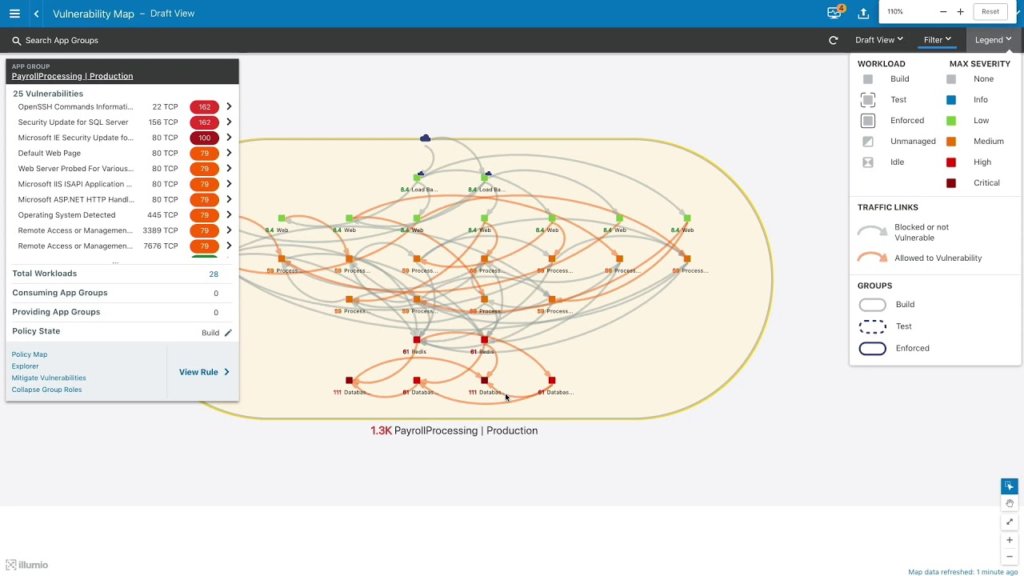
Illumio Core is a CWPP security tool developed to stop lateral data movement. It offers control and management of your organization’s cloud environments and data centers to actively monitor and draw conclusions from relevant metrics related to application interactions within cloud environments. This includes monitoring communication between virtual and physical machines within the cloud ecosystem along with data access and cloud use.
Pros:
- Easy implementation
- Responsive support
- Excellent micro-segmentation technology
Cons:
- Price can be prohibitive for some organizations
- User experience felt unpolished to some
- Lacks developed support options for application-level protection
9. Orca Security
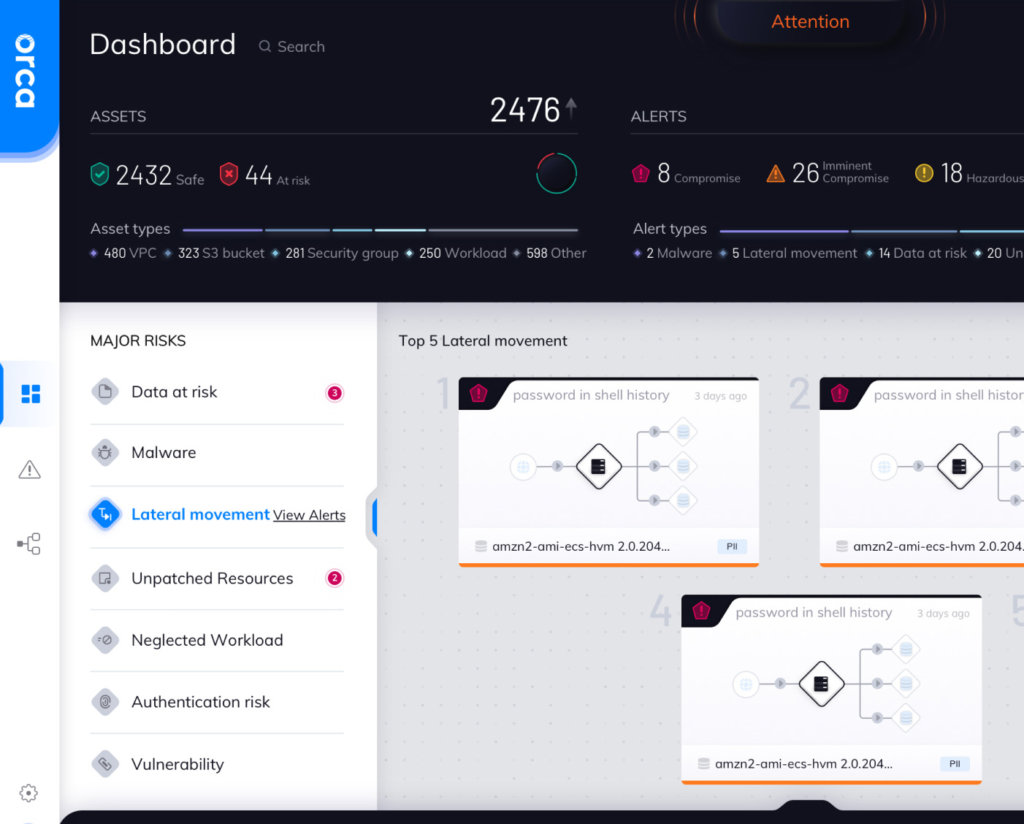
Orca Security is a SaaS-centered workload security tool designed to work with Azure, AWS, and GCP-based cloud networks. The solution is based on the detection and removal of security gaps necessary for third-party agents to be involved in the security process. The focal SideScanning function throws an expansive net over potential misconfigurations and vulnerabilities and detects malware, risky passwords, and high-risk data.
Pros:
- Quick visibility into cloud security posture without agent deployment
- Deep insight into in-container package installs and user access
Cons:
- UI and reporting features are somewhat rough
- Use is not necessarily intuitive to maximize the solution’s capabilities
- Missing legacy and on-premises monitoring
What are Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) tools?
CIEM is a cloud security tool-type intended for managing Identity and Access Management and the complex security conundrum it creates. CIEM solutions are designed to help manage the identity lifecycle and access controls while removing redundant entitlements and enforcing proper access controls. These tools minimize the necessity for human involvement in their operation, reducing time investment and the need to detect over-entitled user access manually.
Top Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) tools
10. C3m – Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM)
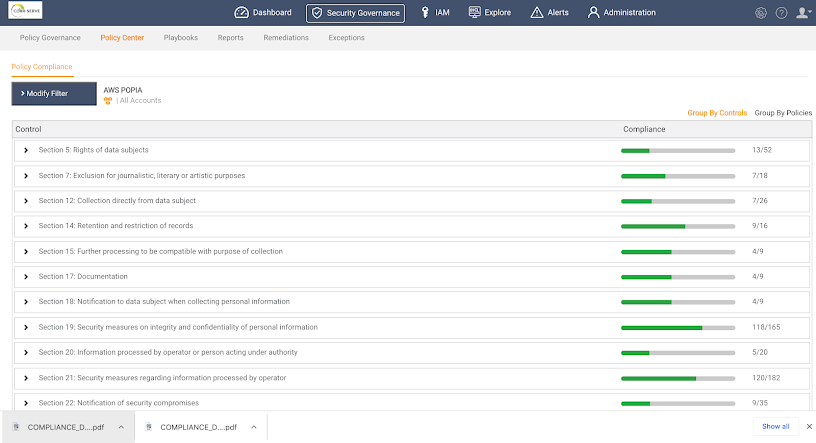
C3M Access Control is a CIEM tool that enables access privilege management and policy enforcement across the cloud infrastructure. It is designed to limit and prevent overreaching user privileges and the detection of potential insider threats. The solution sifts through every identity on your network and determines all the relevant access metrics for each, and automatically alerts and plugs any holes found.
Pros:
- Easy and seamless integration with several other tools
- Ease of deployment
- Simple and effective dashboard
Cons:
- Interface can be buggy at times
- False positives on some cloud assets
- May alert for issues but not always remediate
11. CloudKnox: Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management CIEM
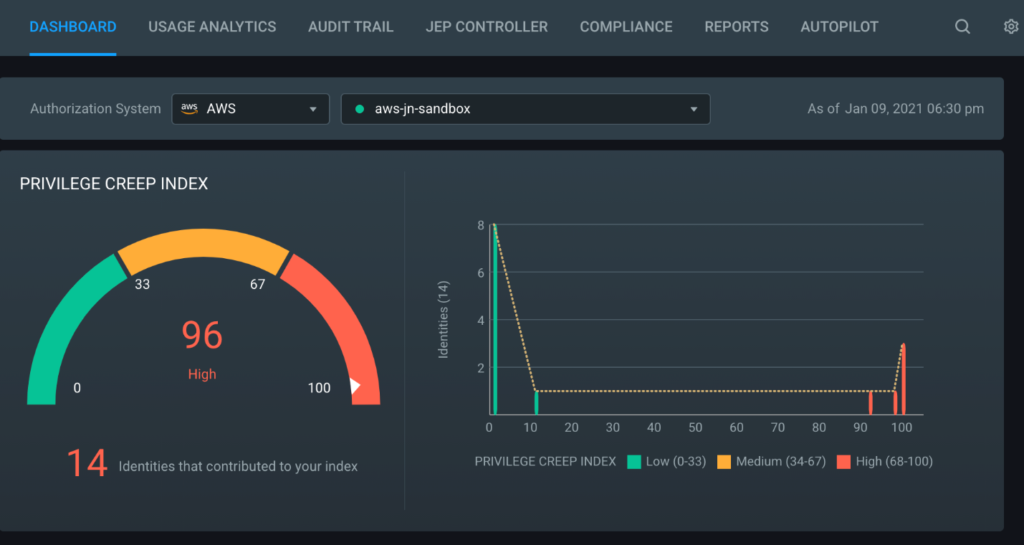
CloudKnox is an efficient and straightforward CIEM solution used to discover the who, what, when, where, and why across your cloud infrastructure. It provides real-time monitoring and reporting of any abnormal activity and management of access policies, including least privilege. There is also an immediate threat response feature and support for all of the popular cloud service platforms.
Pros:
- Efficient visibility and access management across the cloud ecosystem
- Real-time reports and remediation
- Excels at the protection of privilege life-cycle for hybrid-cloud environments
Cons:
- No free trial or version
- The dashboard can feel dated and simplistic at times
How to select the cloud security tools you need
Identify requirements
The first step on your journey to finding the right cloud security solution is to identify the features and requirements for your organization. This is limited to product features and includes, for example, what your budget is, and what level of overhead is comfortable for your organization?
All of this process begins with an in-depth security audit of your cloud ecosystem. You need to have a holistic understanding of your organization’s cloud “pain points.” How exposed would you be if one of these applications or services were no longer secure and exploited? This baseline can identify which cloud security solutions protect those points.
Part of that risk assessment is also in understanding the cloud usage needs of every dev team and project. This includes considering any necessary compliance standards and protocols that you wouldn’t rely on cloud services for their operations.
Identifying your requirements also comprises how hands-on or automated your security tool will be and how simple or comprehensive a solution you need. With various apps in your cloud stack, the last thing you want is one more link in the winding chain that still leaves you vulnerable. Furthermore, if you plan to use multiple cloud security tools, ensuring compatibility is a top priority.
Define your architecture
Once you establish your organization’s baseline requirements for your cloud security, you will have a much clearer picture of what your cloud architecture will look like in operation. It also requires examining which applications you will need to secure, like Office365 and Slack, and your organization’s position on Shadow devices. These different services also come with unique security requirements.
IaaS services require the most legwork and oversight by your organization, as does the responsibility for securing these assets, along with data, user access, the OS, applications, and virtual network traffic. To secure IaaS assets, your organization should ensure they have network segmentation, intrusion detection and prevention, and virtual firewalls and routers as part of your cloud security solution.
SaaS and web services present similar challenges and responsibilities in that the service provider handles the majority while users protect their data and user access. SaaS and web services need alerts and logging and gateways for APIs to keep that aspect of your cloud infrastructure safe.
Last, for PaaS, security for applications, data, and user access falls with the customer, while providers protect the physical infrastructure and operating system. PaaS services require very similar security controls to SaaS and web services, and its primary role is data security. One additional element to consider is what capabilities a security solution offers in the case of a cloud provider outage.
Depending upon your reliance on one or multiple types of cloud services from those listed, specific tools will be much more relevant for your stack. SaaS-heavy, web service reliant, and remote-work oriented entities would do well to include SAST in any cloud security arrangement they decide upon.
Assess the security controls & identify control gaps
As your cloud stack sprawls ever taller and your system more interconnected, the greater the number and likelihood of risks and vulnerabilities appearing. Cloud services are not limited to being accessed by computers at a physical location. Each device used to access the same information may require different security controls to ensure your data and cloud ecosystem remain safe.
This is an instance where gap analysis is critical to ensuring you can properly detect and remedy vulnerabilities quickly and figure out which tools will serve your needs. Assessing your security controls requires accounting for both the services and applications in use today and those you assume and plan on using in the future.
When you are building a cloud security stack, this is also one reason it is best not to approach the issue as filling gaps. With the requirement and architecture in mind, build a comprehensive cloud security framework that considers these assessments.
SAST credential security and privacy with Spectral
A SAST solution provides a safety net that captures sensitive secrets such as Passwords, API keys, security tokens, and other security credentials before they become publicly exposed due to human error or malicious activities. Such credentials may be lurking in places you least expect, including public code repositories, log files, server configuration profiles, and even team communication management solutions such as Slack. Spectral is a SAST solution that continuously evolves through the use of AI and machine learning algorithms. Spectral is a future-safe solution that recognizes new threats as they develop and reduces false positives reports through ML reinforcement feedback.
Deploying SAST in your organization can mean the difference between stable operations and a data breach that you may not recover from, or at the very least may cost millions in remediation. Investing in credential security automation is increasingly becoming a part of every modern DevSecOps that values reliable operation. Make it a part of yours.


