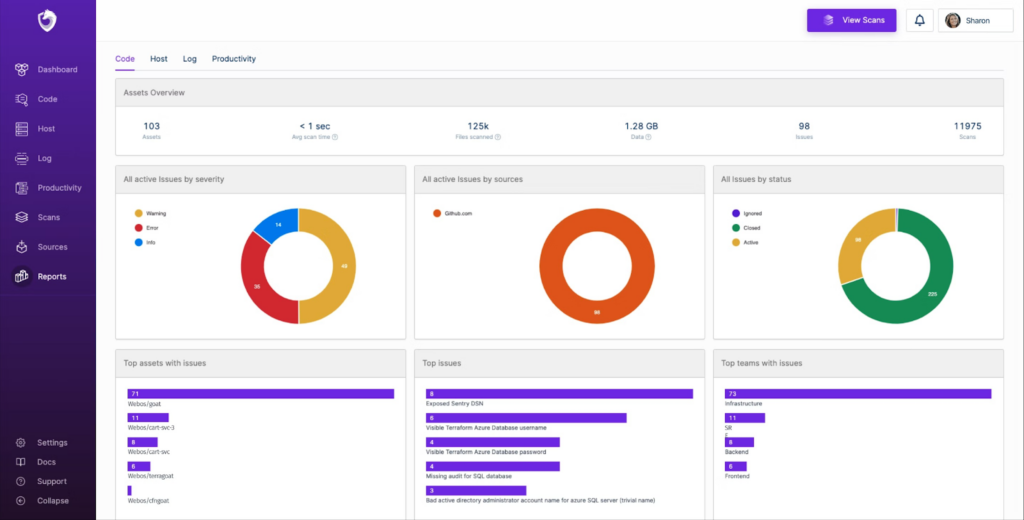
Top 12 Open Source Code Security Tools
Open source software is everywhere. From your server to your fitness band. And it’s only becoming more common as over 90% of developers acknowledge using open
In a world where data is the new currency, understanding and leveraging data monitoring has become indispensable. Data monitoring involves systematically collecting, analyzing, and managing data to uphold its quality, security, and compliance—a critical process in a world where data influences every decision and innovation.
As data management evolves with emerging technologies, cybersecurity threats, and regulatory demands, effective data monitoring becomes a strategic enabler. It empowers businesses to turn data into actionable insights, make informed decisions, manage risks, align with compliance standards, optimize operations, and maintain a competitive edge. companies that adopt data-driven decision-making are 5-6% more productive and profitable than their competitors.
Why is understanding and effectively implementing data monitoring so crucial for your business’s growth and success? Let’s start with the basics.
Data monitoring is fundamentally about three principles: accuracy, timeliness, and comprehensiveness:
For IT professionals, managing diverse data types, each with its own format and complexity, presents technical challenges. Particularly with sensitive data like PHI or financial records, adhering to strict compliance and careful handling is paramount.
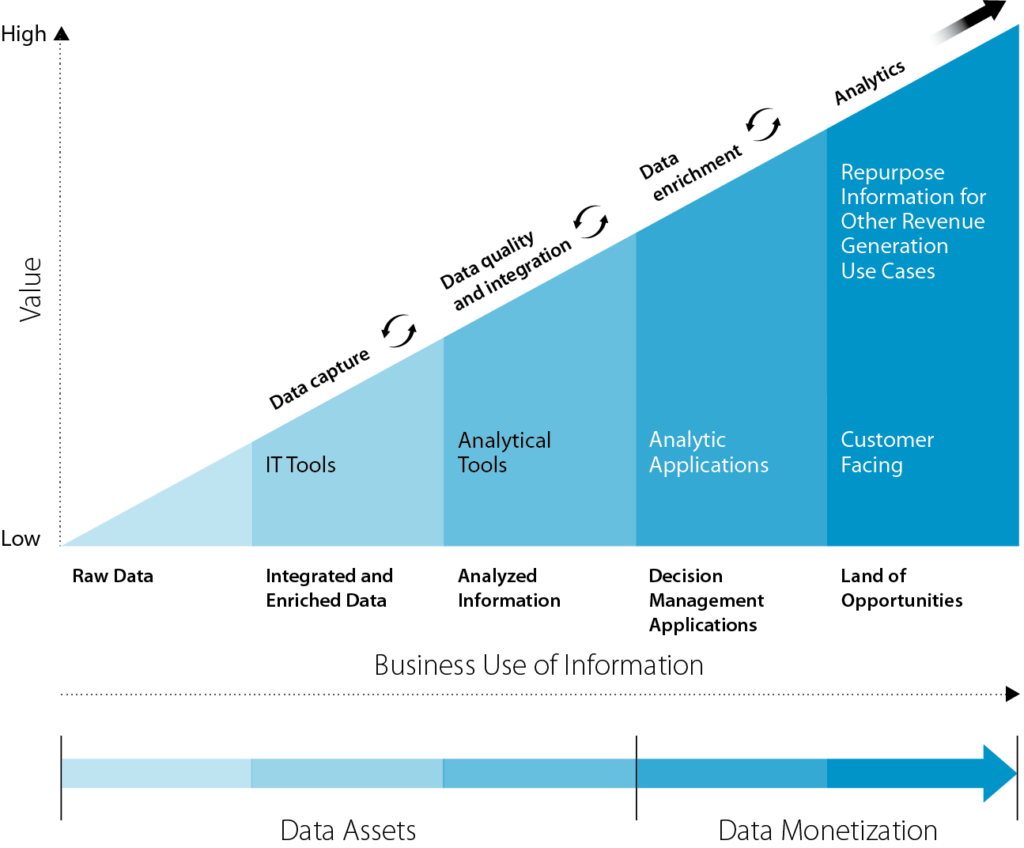
Data monitoring is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses the 3 pillar processes of data collection, thorough analysis, and ongoing monitoring.
The process involves various techniques such as gathering direct user feedback, leveraging automated scraping for vast data sets, analyzing system logs, and harnessing sensor data. Automated scraping excels in large-scale, continuous data collection, whereas direct user inputs shine in acquiring detailed, qualitative insights.
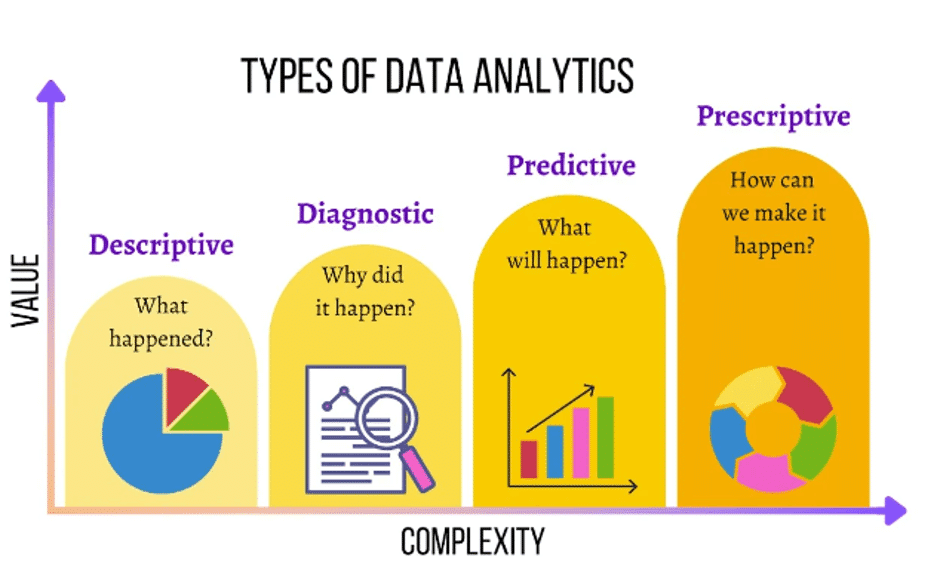
In this phase, the raw data undergoes transformation into actionable intelligence. It’s about delving into the data’s deeper context, exploring how different data points interconnect, and deciphering the implications of these patterns for your business. The tools employed can vary from straightforward statistical software for identifying trends to sophisticated platforms capable of predictive modeling and harnessing machine learning.
In this final stage, the intricate data analyses are synthesized into clear and understandable reports, aimed at facilitating informed decision-making. These reports distill complex data findings into accessible insights, aiding leaders and stakeholders to steer the organization toward strategic goals and ongoing enhancement.
Implementing and sustaining effective data monitoring systems can be challenging due to issues like data silos, privacy concerns, and technological limitations. Tackling these hurdles requires a blend of strategic planning and technological innovation.
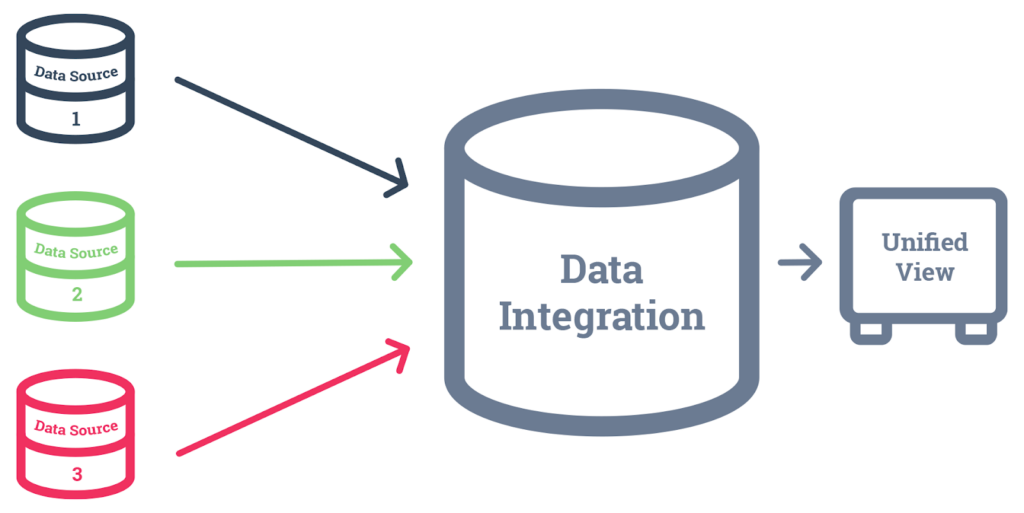
How do the various data monitoring tools, each with their own strengths and limitations, shape best practices in data monitoring, especially within cloud environments? Let’s explore these tools and discuss their roles and effectiveness.
A diverse range of tools is available, each catering to different aspects of data monitoring.
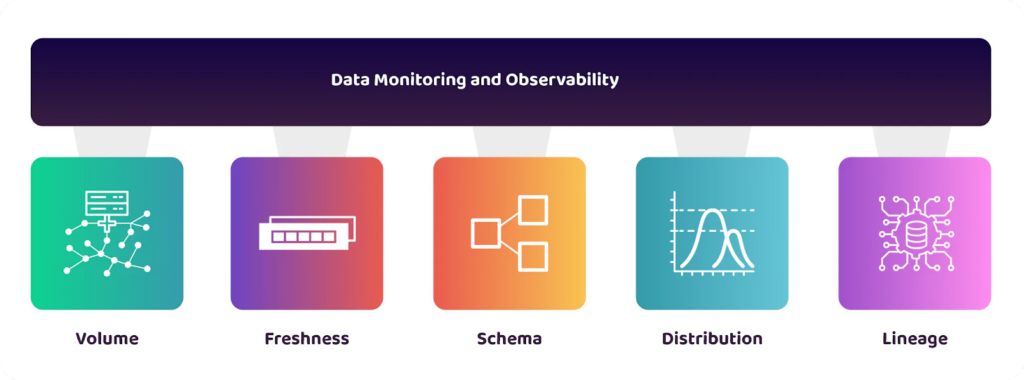
When selecting data monitoring technologies, understanding the strengths and limitations of each is crucial for aligning them with your business needs and cloud environment. In a cloud context, the choice of technology depends on factors like the scale of your data, the complexity of monitoring needs, and the specific challenges of your cloud environment.
| Pros | Cons | |
| Basic Analytical Tools | User-friendly, affordable, ideal for basic data tasks and small businesses. | Limited analysis scope, not for large or complex data, lacks advanced features. |
| Advanced AI-Driven Systems | Handles large data volumes, provides deep insights, suited for complex analysis. | Costly, resource-heavy, requires specialized skills, overly complex for basic needs. |
| Cloud-Native Monitoring Tools | Scalable, flexible, integrates well in cloud environments, handles dynamic workloads. | Needs cloud-specific skills, potential vendor lock-in, less effective outside cloud. |
| Hybrid Monitoring Solutions | Versatile for on-premises and cloud environments, suitable for hybrid infrastructures. | Complex setup and management, may lack some cloud-native features. |
| Open-Source Monitoring Tools | Free or low-cost, customizable, strong community support. | Requires technical know-how for setup and upkeep, dependent on community/vendor support. |
Optimizing data monitoring in cloud environments is crucial, and a few strategic practices can greatly enhance this process. Implementing these best practices establishes a strong data monitoring framework in the cloud:
As we draw this guide to a close, we reflect on the transformative power of data monitoring. It empowers better decision-making, enhances operational efficiency, and sharpens your competitive edge.
As you reflect on your current data monitoring strategies, consider the potential that advanced tools and practices bring to the table. These innovations are not just about keeping pace with data trends but are about staying ahead and leveraging data to its fullest potential. Embrace the advanced capabilities of tools like SpectralOps, and position your organization to make more informed decisions, respond faster to market changes, and maintain a competitive advantage.
Take the next step and explore how SpectralOps can transform your data monitoring strategy today.

Open source software is everywhere. From your server to your fitness band. And it’s only becoming more common as over 90% of developers acknowledge using open

It’s easy to think that our code is secure. Vulnerabilities or potential exploits are often the things we think about last. Most of the time, our

Experiencing a data breach is never pleasant. Just ask any of the hundreds of businesses that suffered a data breach in the past year, exposing billions