Cryptography and network security: The quick and short guide
There is an old joke among cybersecurity professionals that the only way to truly secure your data is to keep it on a machine without connection
Your app is secure, right? Think again.
There are at least 10 vulnerabilities that could be lurking in your code, waiting to be exploited. This reality underscores the importance of mobile app security in the dangerous world of today.
The 2024 Verizon Mobile Security Index revealed that 62% of business network authentications now come from mobile devices. This, along with the widespread use of remote work models, makes mobile apps an important way for hackers to get into networks.
Fortunately, by identifying and tackling the top 10 mobile security vulnerabilities outlined by the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP), you may greatly strengthen your app’s defenses and safeguard user data.
OWASP is an open-source organization, developed for the sole purpose of securing modern-day applications. OWASP was launched 22 years ago and has since become an industry standard releasing updates on the most common vulnerabilities mobile and web applications face today.
OWASP collaborates with 40+ organizations across the world to identify mobile vulnerabilities and releases the “OWASP Mobile Top 10” highlighting the top 10 mobile application vulnerabilities.
Several incidents due to mobile application vulnerabilities have occurred over the last 6 years. Some from large companies affect millions of users across the world. One of the most prominent is the British Airways Mobile app breach, which affected not only the application but its website as well.
In 2021, a mobile application used across the U.S. for parking management, ParkMobile, was breached, exposing the Personally Identifiable Information(PII) (email addresses, phone numbers, license plate numbers and vehicle information) of over 21 million users.
The threat actors exploited a vulnerability in a third-party solution used in the applications’ infrastructure, granting the actors access to its database containing all its users’ data.
The breach raised concerns not only due to the number of customers affected but also the amount of stolen PII and their possible usage: Phishing attacks, identity theft, etc.
In 2018, approximately 400,000 British Airways customers were affected by a breach of its customers’ PII stolen.
The threat actors accessed the mobile app’s backend through an unsecured third-party vendor account with no multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Using these administrative credentials the attackers found plain text files containing approximately 100,000 payment card details of its customers.
British Airways was fined 20 million pounds for this breach. Drawing international attention due to the scale of the attack and exploitation of systems British Airways was unaware of.
The “OWASP Mobile Top 10 2024” highlights the most common and current vulnerabilities faced by modern mobile applications:
Table of contents
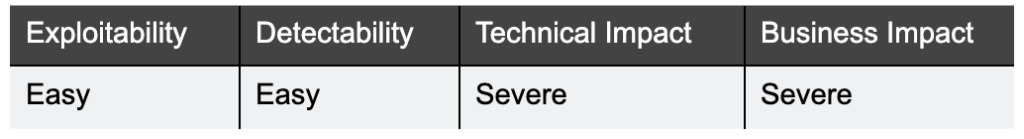
What it is:
This vulnerability relates to hardcoded credentials, insecure credential transmission and insecure credential storage. An example of this vulnerability is the British Airways breach.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
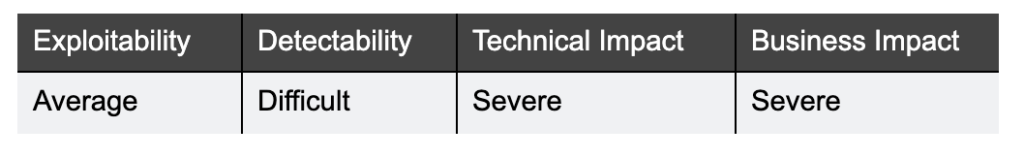
This risk targets SDKs, third-party libraries, vendors, credentials as well as any external systems the app interacts with. If the supply chain is compromised it could allow threat actors to inject malicious code, create backdoors and even take over the mobile app.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
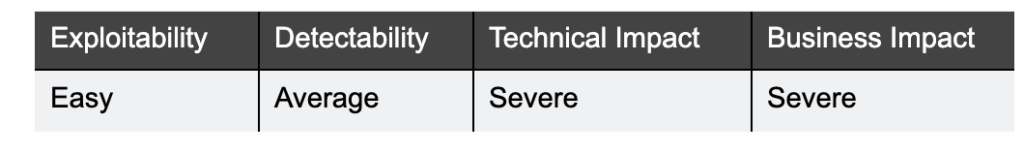
What it is:
Once threat actors find any vulnerabilities in either the authentication or authorization scheme, they can exploit it in two ways:
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
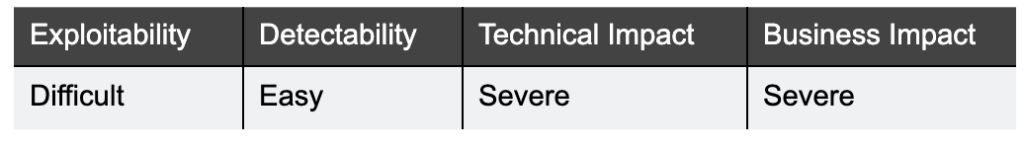
Failing to validate and sanitize input/output data, puts your application at risk of being exploited by attacks: SQL injections, Command Injections etc as well as your application inadvertently exposing confidential data.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
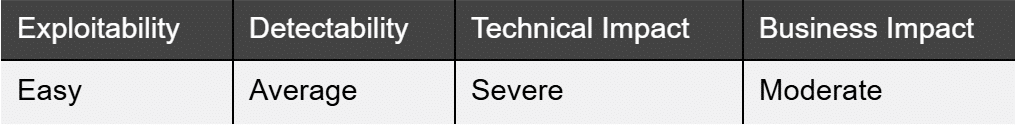
What it is:
Most modern applications use some level of cryptographic protocols. However, there may be flaws in implementation: depreciated protocols, accepting bad SSL certificates or inconsistencies (partially encrypted workflows). Any of these flaws could allow threat actors to intercept communications.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
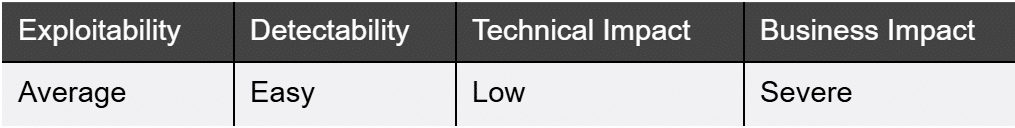
What it is:
This vulnerability focuses on how this PII is stored and transmitted by your mobile application. Breaches resulting in the theft of PII not only affect your users but also have heavy regulatory and financial consequences.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
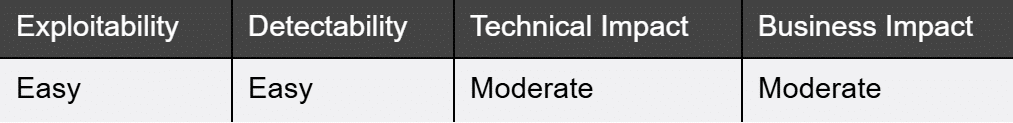
What it is:
All mobile applications are vulnerable to binary attacks. Binary attacks can occur in two types: reverse engineering(decompiling and scanning the application for secrets, algorithms and vulnerabilities) and code tampering (removing licenses, circumventing paywalls…).
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:

What it is:
“Security Misconfiguration” is the eighth vulnerability in the “OWASP Mobile Top 10”. This vulnerability exploits mistakes in configuration due to human error.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:

What it is:
From poor data encryption to insecure secure data storage practices. This risk exploits vulnerabilities that could expose stored data.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
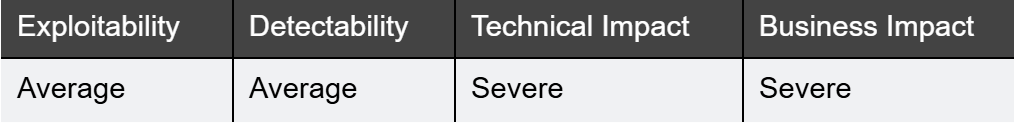
What it is:
This risk exploits vulnerabilities that expose stored your mobile application, through flaws in cryptographic implementation.
How to detect it:
How to prevent it:
The OWASP Mobile Top 10 lists from 2016 and 2024 show big changes in mobile security risks. This development emphasizes the importance for developers and organizations to monitor mobile dangers and change their security practices.
Merged(2016) : Insecure Authentication (M4) & Insecure Authorization (M6)
Merged(2016) : Code Tampering (M8) & Reverse Engineering (M9)
Rewording(2016) : Extraneous Functionality (M10)
We have explored how OWASP Mobile Top 10 vulnerabilities help DevOps teams identify and address major security issues in mobile applications. Understanding these vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and available remediation options allows you to proactively strengthen your mobile security.
However, security is an ongoing journey, not a one-time event. Consider leveraging advanced security platforms like Spectral to stay ahead of evolving threats. By automating security testing, providing real-time alerts, and continuously monitoring your codebase, Spectral empowers developers to deliver secure and reliable mobile applications..Take the first step towards a more secure mobile future. Schedule a demo with Spectral today.

There is an old joke among cybersecurity professionals that the only way to truly secure your data is to keep it on a machine without connection

If developers one day considered security a mere ‘good-to-have,’ that day is firmly in the past. As digital transformation accelerates, employee workstations become liabilities for enterprise

Security is the biggest threat facing organizations that strive for faster software delivery. Organizations are witnessing increasing attacks due to application code gaps and security weaknesses.