Top 12 Open Source Code Security Tools
Open source software is everywhere. From your server to your fitness band. And it’s only becoming more common as over 90% of developers acknowledge using open
Time, cost, and quality – hitting this trifecta is the ultimate goal of any software organization. Its pursuit over decades has resulted in multiple application development methodologies like serverless computing, an emerging and popular cloud computing model touted as the future.
Nearly 70% of organizations will increase their usage of serverless computing by 2025. While serverless architecture offers several benefits, like reduced operational costs and agility, it is also prone to frequent cyberattacks. As with any new application development innovation, more contemporary security challenges arise, and attack vectors constantly evolve with development practices.
This blog post focuses on serverless security, its challenges and benefits, and some best practices to harden your serverless application. Let’s dive in.
Serverless security is a layer of protection aimed at code functions. It is applied directly to the applications, enabling developers to enforce compliance for enhanced security posture. But to understand its significance, let’s take a step back to learn about serverless architecture.
Serverless architecture is a software development approach where you design and run your application without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Your team will only handle writing and executing the code, while your cloud provider will facilitate the application’s servers.
In the early days of software development, you had bare metal servers managed by system admins to deploy applications. It was not resourced extensively but was costly. However, innovations in cloud computing, virtual machines, and containerized applications made building applications flexible, easy, and fast. Serverless computing is like the next movie in the franchise.
The purpose of servers is to facilitate interaction between users and applications. Although essential, servers add quite a bit of complexity, IT operations overhead, and cost. On the other hand, the serverless architecture enables developers to focus on writing quality code instead of maintaining servers, creating backups, and ensuring security. It’s more economical since you only pay for the services you use and use them only when running the application.
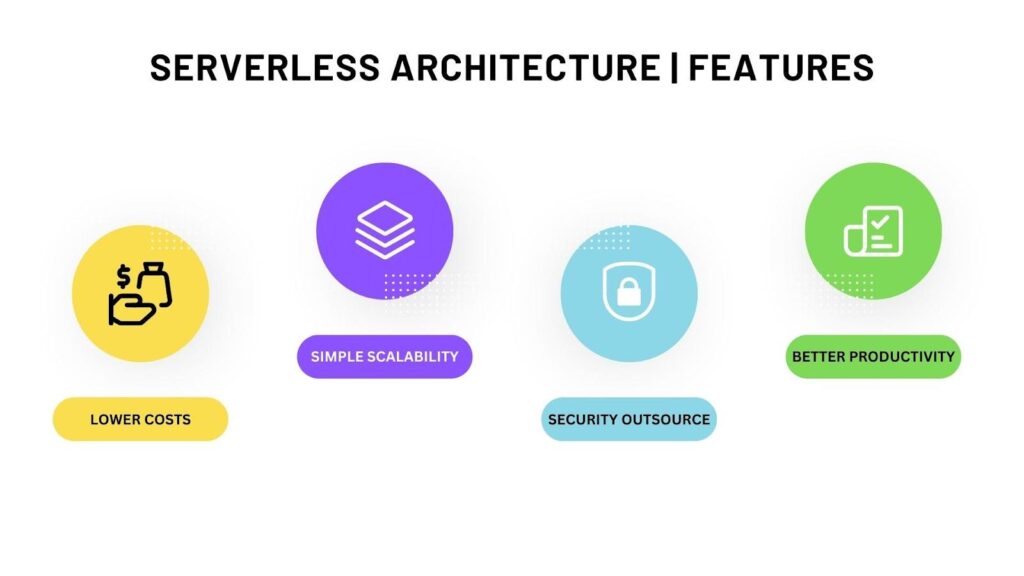
With a serverless architecture like Function as a Service (FaaS), you can write your code as small bits of functions that run when triggered by an event. But the deal is that you also hand over the security to the cloud service provider, which is helpful. With serverless architecture providing automated workflow, you get scalability, faster application delivery, and reduced development costs.
Serverless architecture is an event-based methodology against stream-based, making it more resilient to failures. So when the application experiences a failure, it impacts the specific event and not the entire log. Here are five other benefits of using serverless architecture.
It’s not all rosy with serverless computing and it has some challenges too.
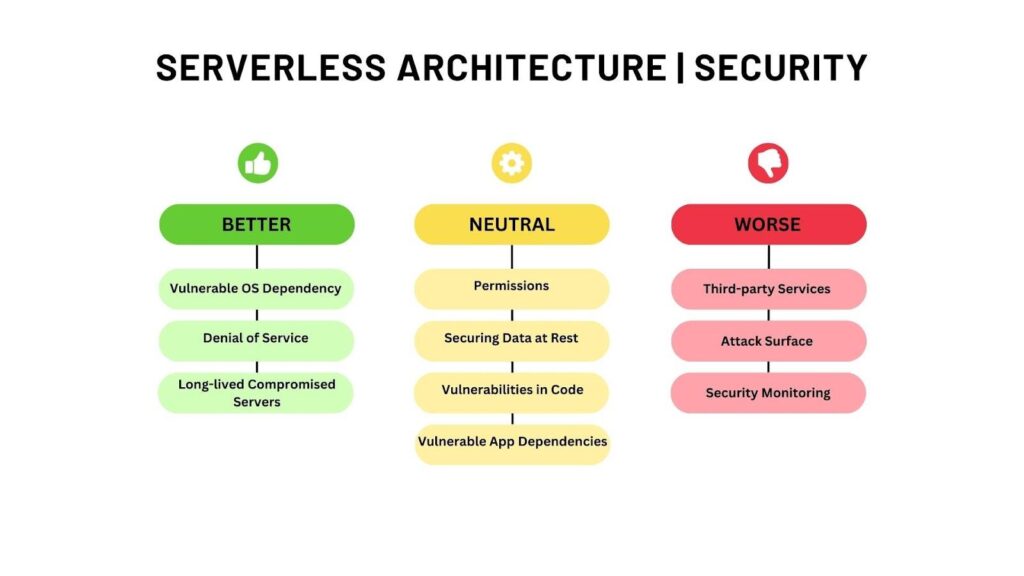
While cloud service providers offer a range of security features and settings, you must configure them properly. Leaving anything out or misconfiguration in any setting can turn into a risk.
The downside of setting individual access to multiple functions is that you could give a user more privileges than necessary. You must always implement least or zero privilege permissions to reduce attack possibilities.
When an event is triggered, it could inject untrusted inputs into the functions. Therefore, you need to carefully assess every event source for illegal data injections.
Neglecting verbose error messages like out of memory, null pointer, multiple other errors, and improper exception handling can give hackers a vulnerability to exploit and launch an attack.
Developers will have to share the responsibility of securing the application along with the cloud providers to tackle vulnerabilities that come with database services, backend cloud services, application-associated configurations, etc.
The features that make a serverless architecture so appealing are also the ones that weaken its security. For example, while the multiple functions of applications enable fine-grained security policy enforcement, they also increase the number of entry points that attackers can target. Protecting your application from attacks means implementing best practices for serverless security.
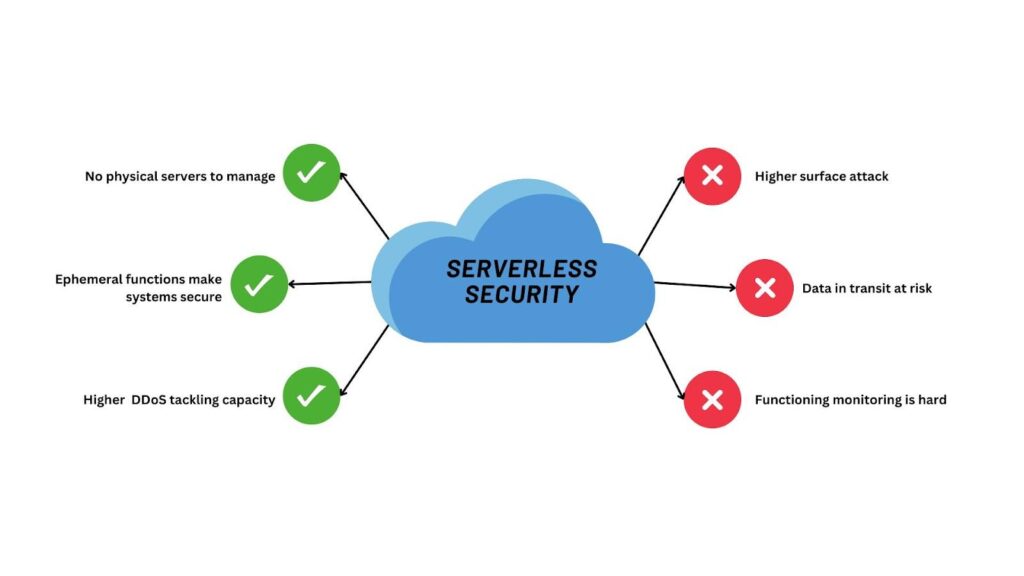
Serverless computing is a unique and powerful software development practice that eases infrastructure management, facilitates scalable applications, and produces quality code. Building a serverless application requires a robust security strategy, including performance tracking and code analysis procedures. In serverless applications, cloud providers protect infrastructure while developers focus on writing and deploying code.
Although cloud service providers offer and implement their cloud security tools and practices, it’s not the end of the road. Developers must claim equal responsibility in hardening serverless security. And for this, you will need third-party tools like SpectralOps, a comprehensive security tool that facilitates code safety and trust through automated processes like infrastructure-as-code scanning, hardcoded secrets detection, and source code leakage detection. It accelerates the implementation of security best policies in seconds by shift-left philosophy.
Request a free demo today.

Open source software is everywhere. From your server to your fitness band. And it’s only becoming more common as over 90% of developers acknowledge using open

It’s easy to think that our code is secure. Vulnerabilities or potential exploits are often the things we think about last. Most of the time, our

Experiencing a data breach is never pleasant. Just ask any of the hundreds of businesses that suffered a data breach in the past year, exposing billions