The DevOps Guide To Vulnerability Management Tools In 2021
Imagine you are in charge of maintaining data for some of the most secretive government offices and powerful business entities globally. You have a significant investment in your security apparatuses protecting that knowledge. For years you haven’t had a single blip or incident to cause any suspicion. Then the unthinkable happens, and from a single weak point, your entire network is compromised by malicious code hidden in an innocuous update.
Now stop daydreaming because this is no fairytale. It’s the briefest of summaries for the SolarWinds supply chain attack that left private, confidential data for over 250 US governmental agencies and global enterprises laid bare. It is also one of many growing costly and painful examples of why vulnerability management has become critical for business success.
Before we offer up a collection of excellent options for managing and fixing your vulnerabilities, let’s dive into exactly what the process is and why it is so important.
What Is Vulnerability Management?
Thousands of vulnerabilities are discovered yearly, and business continuity continues to become hinged on the continual network, process, and software uptime. Organizations need to invest time and effort into understanding where their weaknesses lie to maintain that status quo and continue running smoothly.
Vulnerability management (VM) refers to the steps taken to detect and discern, classify, prioritize, and then resolve vulnerabilities within an organization’s digital infrastructure. This includes cloud and end-user and enterprise software, internet browsers, and more.
This process is not static but a real-time effort to constantly detect and resolve these vulnerabilities. It is done through a combination of consistent patches and reconfiguration of security controls. And it all begins with seeing the weak points within your digital assets and gathering as much information about them as possible.
Vulnerability Identification
You can’t defend against what you can’t see, or in this case, identify. The base of any vulnerability management solution is the scanner that finds those weak points.
How does it work? The process begins with the pinging or sending of TCP-UDP packets to network-connected devices and identifying any open ports or services. The scanner then attempts to access each device and record as much system data as possible before comparing and analyzing that with current known weaknesses. This scan includes user privileges, network infrastructure, security protocols, patch levels, file system structure, IP configuration, etc.
Vulnerability Evaluation
Once vulnerabilities have been detected and identified, the next step is to evaluate their potential risk and deal with them according to your risk management policies. Vulnerability management solutions present these results as risk scores and ratings such as CVE and CVSS.
These scores provide a straightforward way for organizations to separate which vulnerabilities are the most critical and time-sensitive to remediate. However, these scores are not the only variable that is part of this process. Organizations need to examine several factors, false positives, the exploit difficulty, the impact on business continuity, existing security controls, and the duration the vulnerability exists.
Vulnerability Treatment
Once you’ve classified and prioritized particular vulnerabilities more than others, the next step is treating and resolving them. Vulnerability management tools offer not only risk scores but also remedial measures that can be taken. These actions can include reconfigured network settings, removal of defunct accounts and applications, patches, and others. We can categorize these methods down further into remediation, mitigation, and acquiescence.
- Remediation is the full fix or patching of a vulnerability and is the ideal choice for most organizations
- Mitigation reduces the likelihood of exploitation or the potential impact of one, which becomes necessary when patches or fixes are unavailable and insufficient
- Acquiescence is simply acknowledging the vulnerability’s existence and that it may not be worth the investment to fix due to its low impact or risk
Vulnerability Reporting
After treating the discovered and categorized vulnerabilities, the final task is to record and report the results. Consistent and uninterrupted vulnerability assessments will speed the process over time and track progress and changes. Vulnerability management tools frequently offer several options to export and visualize the results of your scans.
Proper reporting will streamline your process and save a lot of time for your IT department by showing them which remediation techniques are most effective. This final step will also help maintain regulatory and compliance standards while monitoring discovered vulnerabilities over time.
Why You Need Vulnerability Management Tools
Vulnerabilities to software and processes are rising, and 2020 showed several alarming trend spikes in the past year. The NVD reported 18,362 new vulnerabilities in 2020, and by mid-2021, there have already been nearly 10,000 fresh instances of discovered exploits.
Considering the trend has been more gradual in recent years, the increasing reliance on remote and cloud-based services for business continuity during Covid-19 can be pointed to as one catalyst. Tying into this trend, secure shell and remote desktop exposure jumped by 40%, which led to the discovery of numerous previously unknown vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities also seem to be aging like fine wine in 2020. A recent report found that 3 in 4 cyber attacks in 2020 used weak points that were two years old, and nearly 20% of the attacks exploited holes over seven years old. Incredibly, the oldest vulnerability detected was over 21 years old.
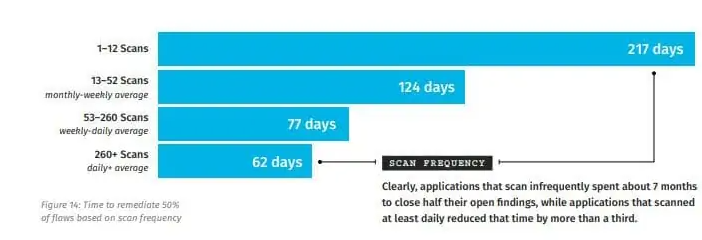
With the number of vulnerabilities growing year-over-year and hundreds of hitherto unknown weaknesses being discovered as well, vulnerability management tools offer a solution to all of these issues, and then some. One straightforward way is through frequent scanning, which can reduce remediation time from 217 days to only 62.
Top 15 Vulnerability Management Tools In 2021
Vulnerability management tools do more than just cut down the time from detection to resolution. They also offer a solution to the cost constraints of maintaining a well-funded IT department by doing most of the work for you. Most importantly, these solutions allow you to get back to work and focus on doing business, not its continuity.
To that end, we’ve collected some of the finest and well-known vulnerability management tools available in 2021, as well as thrown a surprise or two in the mix.
Flexera – Software Vulnerability Management
Flexera offers live updates as well as vulnerability identification and patching for non-Microsoft applications for Windows-based terminals. Flexera combines vulnerability management with security patch supervision and implementation while providing insight into threats and their remediation priority.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- Excels at helping maintain compliance in a proactive manner
- Patch automation features simplify and streamline vulnerability remediation
- Creates blueprint to be applied to current and future vulnerability remediation
Cons:
- Dashboard design gives the impression of results being overwhelmingly negative
- Patchy technical customer support
- More expensive compared to many other options
- UI can get slow at times
SpectralOps
Spectral might not be the first solution you think of for vulnerability management, but it offers a powerful solution for code and asset scanning for credentials and hidden information. Spectral excels at vulnerability management in the human sense, as it combats the potential for errors when it comes to secrets and credentials within your code.
Spectral offers automated code security along with scanners to actively monitor and protect tokens, API keys, and credentials while thwarting high-risk misconfigurations. This DevOps VM solution will boost your DevSecOps processes and efficiency with our automated secret protection and eliminate blind spots and gaps with real-time scanning.
Price: Upon request, free trial on the homepage
Pros:
- Standard-sized code repositories can take under a second to scan
- Flexible platform is highly customizable and optimized
- Mitigates misconfigurations and exposed secrets in real-time
- Completely automated setup process
- 200 custom and tuneable detectors fortified with AI and machine learning models
Snyk
Snyk is another developer-oriented security tool that is relevant for organizations consistently utilizing open-source code. It focuses on the proactive search and remedy license violations and vulnerabilities in open source Docker images and dependencies. Snyk also features a proprietary vulnerability database that is consistently maintained and updated.
Price: Starts at $195 per month
Pros:
- More developer-friendly than other traditional options
- Built-in integration for CI/CD pipeline
- Responsive support staff
Cons:
- Report generation and subsequent visibility are a bit lacking
- The sheer number of integrations causes some users to get lost trying to understand and find the relevant ones
- Lack of simple set up, tutorial materials to independently deploy tool
- Information management filters can use improvement
ThreadFix Vulnerability Management Platform
ThreadFix is a VM solution that bridges the gaps between app developers and security teams, along with the rest of your organization. It provides a reliable asset management tool that can track and optimize the compliance and certification process. It also synchronizes vulnerability tests from several sources, making the tool excellent for larger enterprises with multiple security teams.
Price: Starts at $2000/month
Pros:
- Supports an array of well-known bug and vulnerability trackers
- Consolidates and removes duplicate reports to keep information management unfettered
Cons:
- Lacks asset discovery and network scanning
- Price model per feature can quickly get expensive monthly
- Lacks cross-platform support
Qualys Vulnerability Management
Qualys is a VM tool that offers organizations of all shapes and orientations security compliance and vulnerability management in one platform. It also features a device mapping feature that provides a visual representation of your network map to examine potential weak points in the structure.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- The vulnerability scanner is very accurate
- Excellent endpoint management features allow for consistent results sans user involvement
Cons:
- Endpoint scanning causes a noticeable lag in performance
- Less intuitive for IT staff that have not used the tool before
- Automatic password resets for admins can be tedious and occur unbeknownst to them
- A few users reported high levels of false positives
Rapid7 InsightVM
Rapid7 has taken the success of their Nexpose product to introduce Insight VM, a vulnerability manager. It offers detail-rich reports and provides a small window into cybercriminals’ minds through its analytics.
Price: $25 per asset/month
Pros:
- Detected weaknesses offer a wealth of information about the problem and methods to remedy or mitigate them
- Once getting used to the platform, it is easy to use
Cons:
- Too frequent console updates causing lockups
- Some scans randomly start running for extended periods, wasting resources
- Periodic console crashes
CrowdStrike Falcon Spotlight
CrowdStrike’s Falcon Spotlight is an enterprise-focused security tool that is part of the CrowdStrike Falcon platform. Its scan-free, always-on, and real-time vulnerability hunting feature offers visibility for your organization’s security teams. Spotlight also offers actionable data on vulnerabilities without having to scroll through hefty reports all through their dashboards.
Price: Starts at $9 per endpoint/month
Pros:
- Includes Zero-day, online endpoint, and ransomware protection
- The agent itself is lightweight and doesn’t interfere with device operation
- It offers the capability to write custom exceptions and block rules.
Cons:
- Every new feature release requires an additional investment
- Mediocre reporting and issues with data accuracy were noted
- Desktop pop-ups can be distracting and intrusive
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus
ManageEngine’s Vulnerability Manager Plus is an enterprise-centered solution that offers real-time visibility and coverage, as well as risk assessments and built-in remediation capabilities. It also includes an audit feature for antivirus, port, and software vulnerabilities on a single platform.
Price: Starts at $695 annually
Pros:
- Includes more features built-in than competitors
- Cross-platform support
- Includes a free version and free trial
Cons:
- Pricing can be prohibitive for smaller organizations
- Risk assignment can be iffy and exaggerated at times
Tripwire IP360
IP360 is a VM solution that comes in a variety of forms that are packaged to appeal to organizations from small businesses to large agencies and organizations. It provides a platform to automatically discover and monitor your enterprise’s digital assets and their relative risk. The scanners can be customized to your specifications and assist in building an efficient vulnerability remediation process.
Price: Starts at $5,811 annually
Pros:
- Automatic updating of vulnerability rules for current and future scans
- Reporting is very informative, high quality, and relevant for several business uses
- Scan scheduling allows for hands-off functionality to limit the need for a human element
Cons:
- Lack of discovery capabilities for other security applications
- Lacks full cross-platform support and no mobile app
- Only on-premise deployment option
Kenna Security: Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Software
Kenna Security is a SaaS-based protection and remediation solution with standard scanners along with predictive risk modeling. This allows for real-time updates of and matching for newly-discovered vulnerabilities and always-on risk assessment. It provides IT security teams an opportunity to focus on resolving risks and consistently reporting on the organization’s security posture.
Price: Starts at $12 per asset annually
Pros:
- Risk reporting and threat intelligence is comprehensive and informative
- Collection of integration support for many popular tools in the field
- Simple cloud-based setup and management
Cons:
- Lack of filters to visualize data collected, and inaccurate modeling
- Connectors offer inconsistent performance
- Dashboard features feel limited
- Lacks certain compliance certifications that can be critical to some organizations
F-Secure Elements Vulnerability Management
F-Secure Elements VM, formerly Radar, is a cloud-based risk detection and management solution that offers scanning and visibility into the digital aspects of your business. It also reports third-party scams, phishing sites, and brand violations. The tool is part of the F-Secure Elements platform that can be acquired as a complete package or singular tools.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- Security reports are high-quality and actionable
- Specializes in automation of various reporting and workflow tasks
Cons:
- No links to knowledge base articles explaining how to fix discovered vulnerabilities
- Scanning intranet servers requires the installation of a separate scanning node
- Cloud-only deployment, no on-premise option
GFI LanGuard
GFI Languard is a patch vulnerability-oriented tool geared towards small, medium, and large organizations. It is honed in on device, patch, and network scanning along with risk analysis from a single terminal. Their new CloudPassage feature for protecting cloud assets along with its ViewFinity identity management tool has been well-received additions to the solution.
Price: Starts at $26 per node annually
Pros:
- Quick and simple installation
- The interface is intuitive, and workflow is easy to follow
- Powerful network scanning features
Cons:
- Onscreen reports, when previewed, are unreadable, only usable downloaded
- Cumbersome UI
- Some users complained of uncomfortable UX
BreachLock
BreachLock focuses on consistent and constant security testing for cloud and DevOps-centered businesses. At its core, BreachLock is a Pentest as a Service that features white hat professionals and AI optimization support.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- Excellent customer support and hands-on assistance
- Accurate vulnerability scanner
- Leverages AI, cloud, and white hat hackers for scalable solution on-demand
Cons:
- Lacks network scanning and asset discovery
Greenbone Vulnerability Management
Greenbone’s VM solution is an open-source-based software with automatic security scans and updates every 24 hours. It is available as a cloud, physical, and virtual-based tool and offers preemptive security reports on vulnerabilities before they can affect your organization.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- An excellent reporting system for both network and vulnerability scans
- Low resource load even when running in parallel with other processes without downtime
Cons:
- Scans take an excessive amount of time to complete
- SIEM integration is a hassle
- No automation options
Beyond Security beSECURE
Beyond Security’s beSECURE dubs itself a self-sufficient vulnerability management solution. It can be fully functioning from boot up within five minutes and can be deployed on-premise, on-cloud, or in a hybrid environment. They are confident enough in their accuracy that they offer a bug bounty for any false positives detected by users.
Price: Upon request
Pros:
- Network scanning runs without agents needed
- Automated pen testing
- Scan creation and management is intuitive and flexible
Cons:
- Challenging to manage access for on-premise installations
- Scans are resource-intensive
Regain Control and Secure Your Digital Assets
Vulnerability Management has proven to be more critical to implement than ever if 2020 taught us anything. The rising number of vulnerabilities, and their cost to organizations, has made it clear it is worth investing in managing potential risks to your business continuity and maintaining deterrence.
Vulnerability management isn’t so straightforward, however, and requires solutions that protect both your applications and devices, as well as your data and the code beneath it. It is just as essential to prevent and actively monitor against human error and misconfigurations, which can be just as costly. Vulnerability Management tools are a vital factor in organizations’ protection of these digital assets now and in the future.