7 Steps to ensure compliance with the CJIS security policy
A high-profile case hangs in the balance. Suddenly, court systems are paralyzed. Evidence is locked away, replaced by a ransom demand. Every law enforcement agency’s nightmare
Imagine a world where you can easily protect your company’s important data while ensuring compliance with strict security guidelines. ISO 27001:2022 promises just that.
Because data breaches are becoming more expensive and cyber threats are growing, companies need to strengthen their security posture. Just in 2024, the average cost of a single data breach reached an astonishing $4.88 million. ISO 27001:2022 offers a proven framework to safeguard your organization’s information assets.
Whether a startup or an established enterprise, learning about the ISO 27001:2022 standard’s key controls and implementation methods empowers you to build a robust security posture and protect your organization’s future.
ISO 27001 is a global standard for the information security management system (ISMS), developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It offers guidance on securing information technology assets, including the establishment, development, integration, operation, assessment, and maintenance of an ISMS against unauthorized access, data losses, and cyber threats.
The purpose of ISO 27001 is to provide a clear, structured framework for managing and securing an organization’s information assets. ISO 27001 wipes out the chances of exposing confidential information to unauthorized access, data leakage, as well as cyber attacks. It also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Implementing ISO 27001 improves businesses’ security practices and provides a competitive edge in the market. Here are 3 main benefits you can get from implementing ISO 27001:
ISO 27001 consists of 2 main parts: 11 clauses and 93 controls from Annex A.
The first part of ISO 27001 consists of 11 clauses. Out of them clauses from 4 to 10 are mandatory for ISO 27001 certification. While Clauses 0–3 are not mandatory, they help organizations understand the ISO 27001 process. Here is a complete breakdown of these 11 clauses:
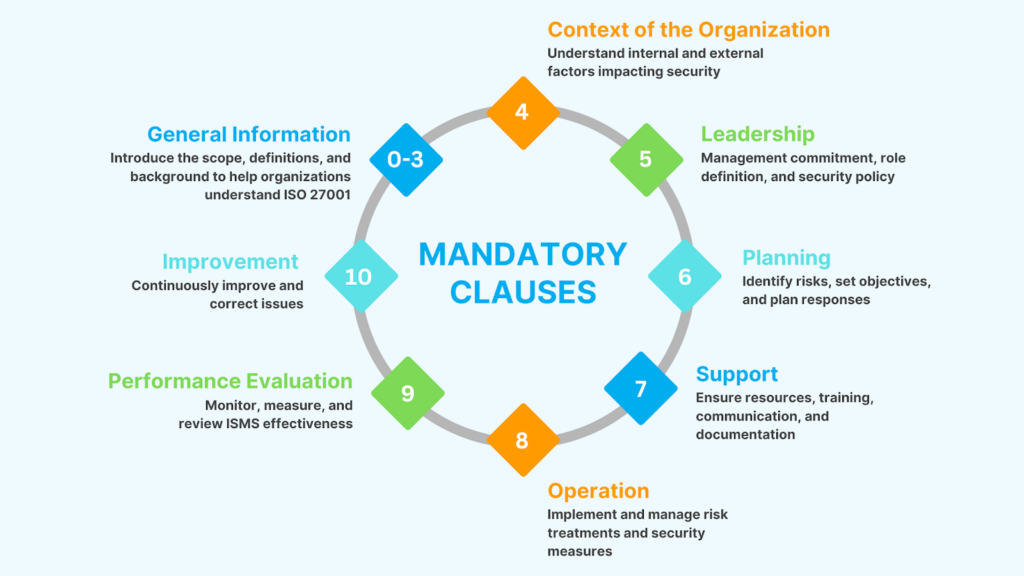
Created by the writer
The second part of ISO 27001 is called Annex A, and it contains 93 security controls under 4 categories:
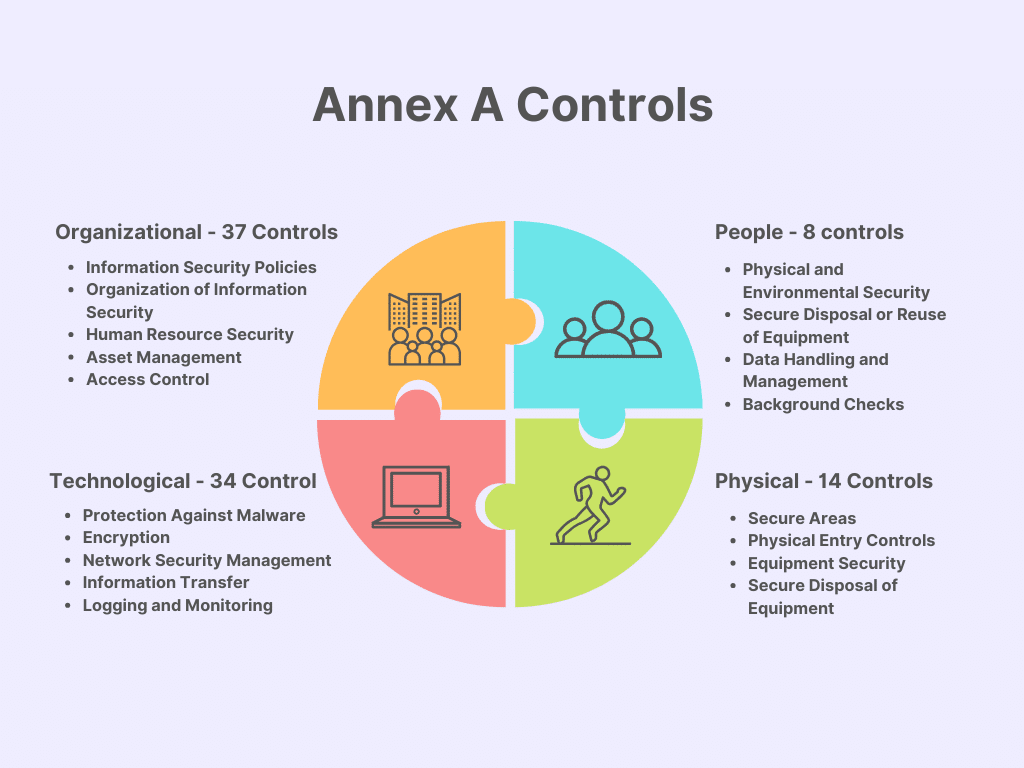
Created by the writer
The Statement of Applicability (SoA) is a key document within ISO 27001 that lists all Annex A controls and indicates whether each control is “applicable” or “not applicable” based on the organization’s specific needs. For each applicable control, the SoA provides a rationale for its inclusion and an outline of its implementation.
The 2022 version of ISO 27001 brought some key changes to help organizations address new security threats. Here’s a look at the main updates:
Since you now have a good understanding of ISO 27001 and its purpose, let’s discuss some of its key controls in detail with purpose, relevance, and real-world examples.
Unauthorized access is a common security issue every organization faces. Proper access control and authentication mechanisms enforce strict access policies, ensuring only authorized individuals access sensitive data.
Implementation Steps:
Employees often make mistakes that can expose systems to phishing, malware, and insider threats. Conducting periodic awareness and training sessions can improve their knowledge of modern attacks and help them easily handle security threats.
Implementation Tips:
Mismanaged assets like untracked devices, software, or network components can create security gaps. Good asset management prevents this by keeping an updated list of all assets, from servers and laptops to software and IoT devices.
Implementation Tips:
Risk evaluation enables organizations to handle security issues by periodically determining, estimating and ranking threats, or vulnerabilities. This permits them to fix the most important weaknesses first.
Implementation Tips:
Incident response ensures that security incidents are contained and resolved quickly. Fast action helps minimize data exposure, legal risks, and operational disruptions, and recover quickly from any issue.
Implementation Tips:
Configuration management makes sure that all systems are properly set up and that there are no hostile settings. Dealing with misconfigurations is critical to the security of an organization as they are one of the major causes of security breaches.
Implementation Tips:
Data masking protects sensitive data in testing, development, and other non-production environments. This process reduces the risk of exposure by ensuring that real data is not accessible where it isn’t needed.
Implementation Tips:
Information deletion securely removes data that is no longer needed. This process prevents unneeded data from being accessed or recovered to protect sensitive information.
Implementation Tips:
By using secure code practices, it reduces the risk of attacks like injection and cross-site scripting, strengthening application security.
Implementation Tips:
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a strategy for making sure that sensitive information is not sent outside of the organization by unauthorized individuals. DLP solutions enforce secure limits on confidential information to ensure that such information cannot be leaked out either by accident or on purpose.
Implementation:
Organizations can develop a strong security posture and protect their precious assets by putting in place the measures defined in ISO 27001:2022. This widely recognized standard offers a structured approach to information security management that will assist you in mitigating risks, ensuring compliance, and building confidence with stakeholders.
However, conforming to ISO 27001:2022 might be a challenging process. With Spectral’s innovative security solutions, you can simplify and streamline your security processes. Our automatic vulnerability assessment and secure coding solutions assist you in identifying and mitigating potential security threats, guaranteeing compliance with ISO 27001:2022 and other industry standards.Looking to level-up security strategy with Spectral? Contact us today to learn how our platform can help you achieve your security goals.

A high-profile case hangs in the balance. Suddenly, court systems are paralyzed. Evidence is locked away, replaced by a ransom demand. Every law enforcement agency’s nightmare

Have you ever built software without encountering a single vulnerability? Unlikely. Vulnerabilities are an unavoidable fact of DevSecOps life, and the stakes are higher than before.

Logs tell the hidden story of your IT infrastructure – what’s working, what’s breaking, and what could be under attack. You’re left sifting through a chaotic