Top 9 Vendor Risk Management Software for Infosec Pros in 2023
No single organization can master all trades, which is why their success hinges heavily on their vendors. And if vendors are crucial for your business operations,
To grasp the concept of a Kubernetes Deployment and Kubernetes Deployment strategy, let’s begin by explaining the two different meanings of the term “deployment” in a Kubernetes environment:
Kubernetes Deployment allows you to make declarative updates for pods and ReplicaSets. You can define a desired state and the Deployment Controller will continuously deploy new pod instances to change the current state to the desired state at a controlled rate.
Running Kubernetes Deployment has the benefit of automating the procedures necessary for scaling, deploying, and updating your applications. This simplifies the process of rolling out new microservices, applications, or updates to existing apps.
By eliminating manual and repetitive tasks, this automation frees up resources within your IT management. The Deployment Controller continuously monitors to make sure the pods and nodes are functioning properly. It replaces or bypasses failing pods and nodes, resulting in quicker deployments and fewer mistakes.
The most typical use cases for Kubernetes Deployments include:
The elements of a Kubernetes Deployment include:
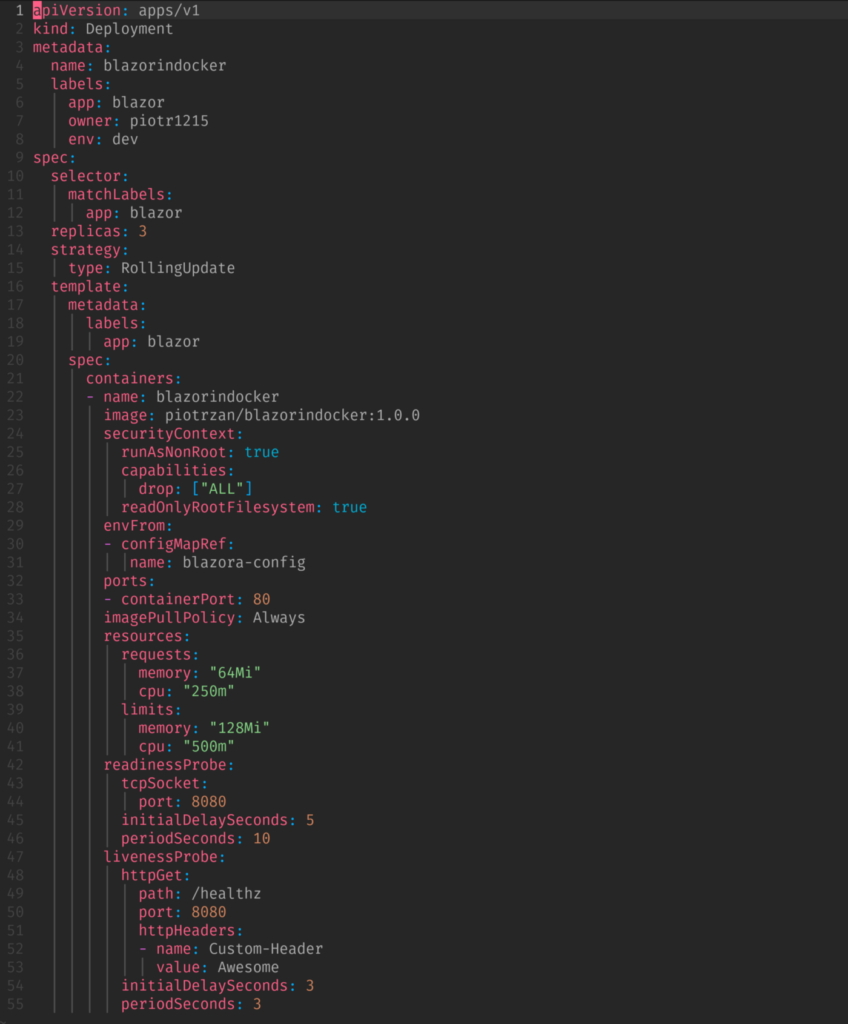
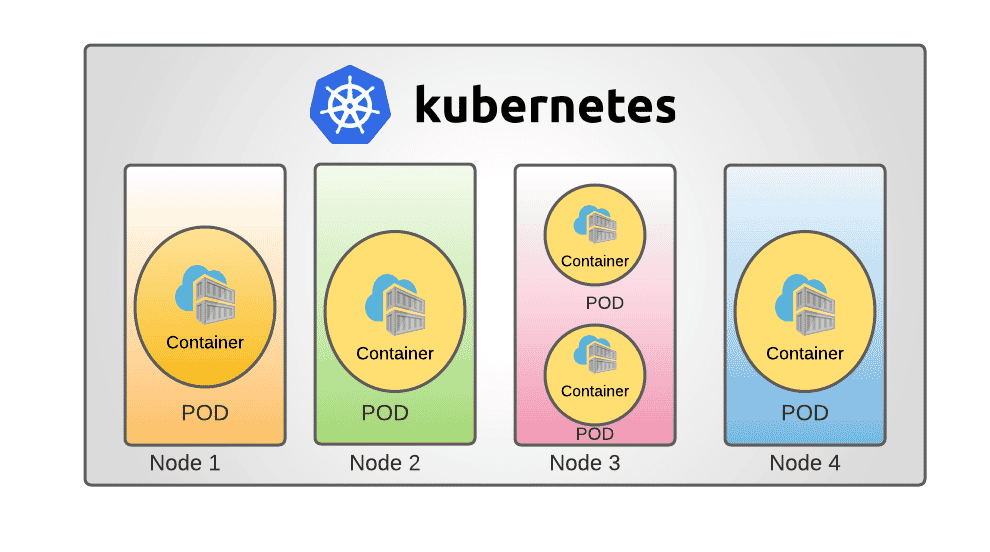
The elements function together for the Kubernetes Deployment in this order:
Step 1: Create a YAML file describing the desired state configuration of the cluster.
Step 2: Use kubectl (Kubernetes command-line interface) to apply the YAML file to the cluster.
Step 3: Kubectl then submits the request to the kube-apiserver, which authenticates and authorizes the request before recording the change in a database.
Step 4: The kube-controller/manager continuously monitors the system for new requests and then strives toward reconciling the current state to the desired state by creating deployments, pods, and ReplicaSets in the process.
Step 5: Once all of the controllers have run, the kube-scheduler will see that there are pods in the pending state because they haven’t yet been scheduled to run on a node. The scheduler finds suitable nodes for these pods, then communicates with the kubelet in each node to take control and begin the deployment.
To summarize, the user sets the definitions using a Kubernetes Deployment, and Kubernetes takes over to ensure that the pods meet these new requirements, implementing any necessary changes.
The ideal outcomes you’ll want to achieve from Kubernetes Deployments include:
A Kubernetes Deployment strategy defines the creation, upgrading, and downgrading procedures for different versions of Kubernetes applications. In a traditional software environment, application deployments or upgrades often result in service disruption and downtime. Kubernetes helps to avoid downtime by providing a variety of deployment strategies that allow you to make rolling updates on multiple application instances.
Kubernetes Deployment strategies support a wide range of application development and deployment requirements. Because each Kubernetes deployment strategy has its own advantages, choosing what strategy is right for you simply depends on your needs and goals. So here is a roundup of seven Kubernetes Deployment strategies that you might want to consider with this in mind.
It is important to realize that only the Rolling and Recreate deployments are default deployments built into the Kubernetes system. It is possible to perform the other types of deployments in Kubernetes, but it will require some customization or specialized tooling.
Kubernetes Deployment strategies:
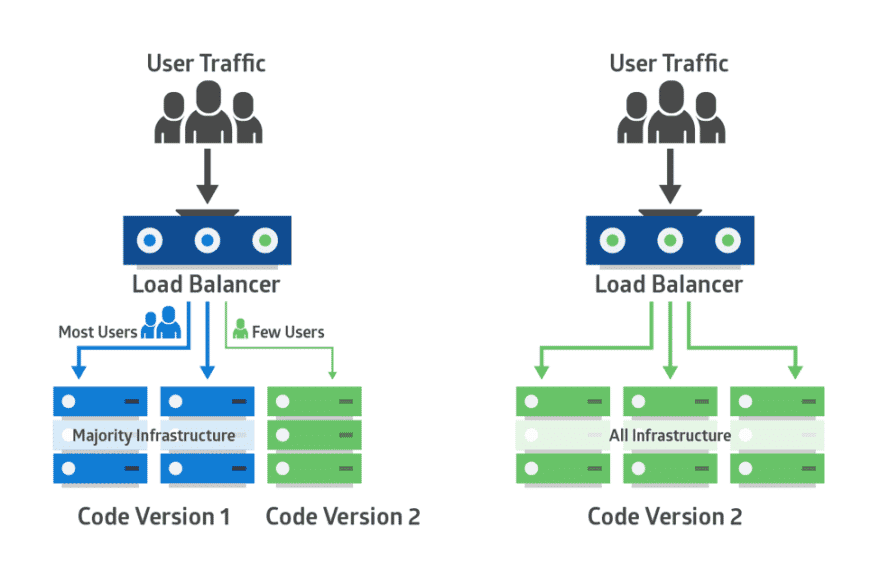
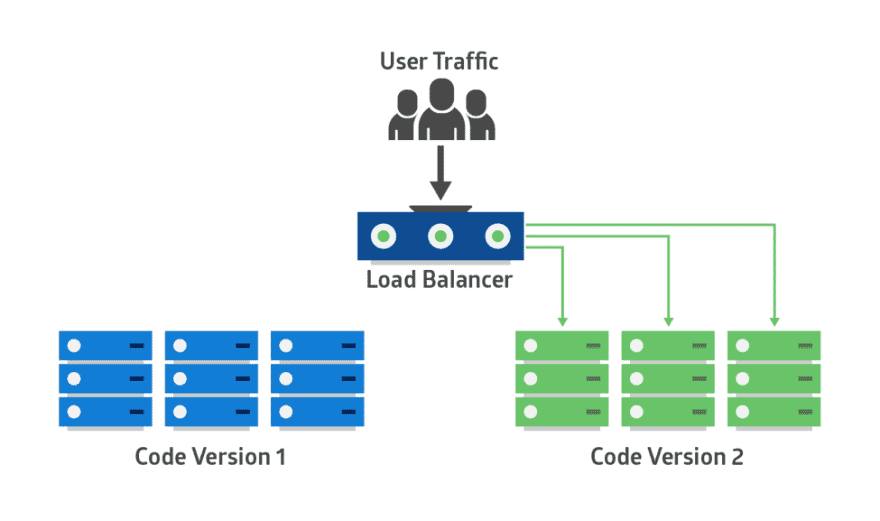
Regardless of whether your goals are to decrease time to market, operate with greater flexibility, create deployments with zero downtime, or release apps and features more quickly or frequently, determining the best Kubernetes Deployment strategy is certainly essential to creating resilient infrastructure and applications.
But what’s it all worth if it’s not protected from the start? It’s important to adopt a DevSecOps approach that incorporates security as a fundamental aspect of all stages in the application development life cycle. Finding security issues as early as possible is the ideal approach. Security issues can undermine the success of your efforts. To strengthen your Kubernetes configurations and ship software quickly and without worry, you can leverage an automated security scanner to find harmful security errors in code, exposed secrets, and other artifacts in real-time. Try it out with a free account today.

No single organization can master all trades, which is why their success hinges heavily on their vendors. And if vendors are crucial for your business operations,

Integration is an indispensable aspect of modern software development. As software applications become more complex and interconnected, every component must work seamlessly together like a game

Modern companies are rapidly adopting cloud applications and services due to scalability, cost savings, and faster time to market. DevOps teams and developers must deliver fast,