There’s one thing every developer should do – prepare for the unknown.
MongoDB is a NoSQL database widely used in web development, designed to handle unstructured or semi-structured data. MongoDB’s core concept revolves around storing data in flexible, JSON-like documents, allowing developers to easily use them for different purposes.
Over 87,000 companies worldwide use MongoDB, and one of the standout features is its robust support for replication. This setup enhances data redundancy and improves failover capabilities, ensuring that applications can function despite server downtime.
This article will take you through implementing a MongoDB replica set to improve your application’s reliability and resilience.
What is MongoDB Replication?
Regardless of your database system, ensuring consistent and high data availability is crucial for any application, and it helps businesses improve the discoverability of their data for analysis. MongoDB replication involves creating and maintaining copies of data across multiple servers, known as replica sets, for data loss prevention.
Why Do You Need MongoDB Replication?
Here’s how MongoDB replication can benefit you.
1. High Availability of Data – All the Time
With MongoDB replication, your application can remain secure, accessible, and functional even during crises. For instance, if the primary server faces an issue, you can promote a secondary server to step up and continue the operations as usual. It is an essential feature for businesses requiring high availability, like financial platforms, e-commerce sites, and games.
2. Data Redundancy
In MongoDB replication, several copies of the same data set are available on multiple servers. This redundancy creates a sort of safety net for the data. For example, administrators can promote a secondary server to continue functionality in case of an issue in the primary data server. Also, these replicas can be specifically assigned for backup and disaster recovery purposes.
3. Load Balancing
You can easily use MongoDB replicas to manage application traffic and distribute workloads. For instance, you can direct read operations to secondary servers, allowing the primary server to focus on write operations and maintain data consistency. In addition, load balancing improves user experience and performance during peak hours by distributing read operations.
4. Geographical Data Distribution
MongoDB replication allows you to create replica sets distributed across geographical regions. If your application is used globally, you can get some significant advantages from this implementation:
- Significantly reduce data retrieval latency by placing replica sets closer to your users.
- In case of a localized disaster, data from a replica set in another region can be used to quickly restore service.
- It’s ideal to keep data within specific geographical boundaries for compliance.
What are the Key Features of MongoDB Replica Set?
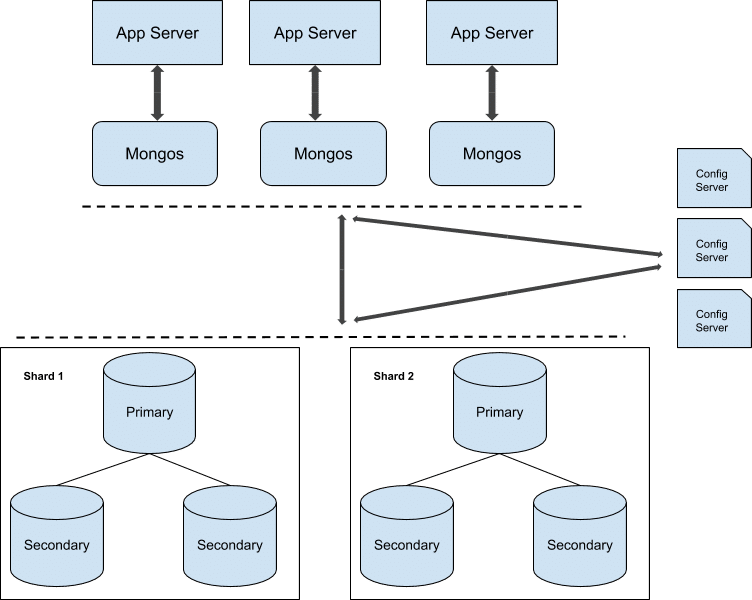
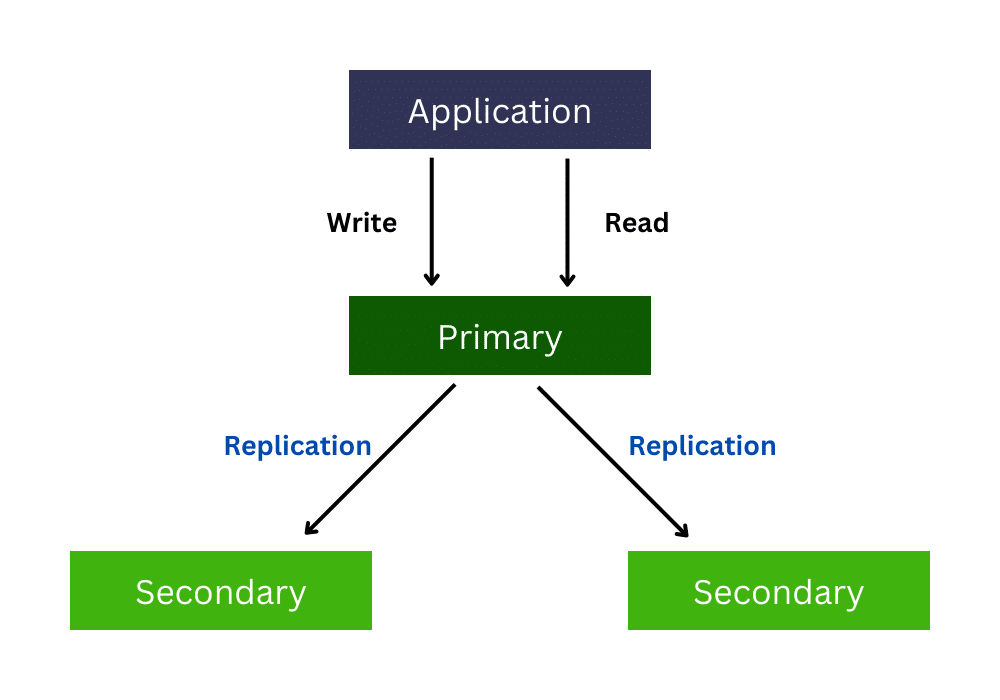
A MongoDB replica set consists of multiple MongoDB instances, each holding the same data where one node acts as the primary node. The remaining nodes, named secondaries, use the primary’s activities to maintain a consistent data set. A replica set includes several key features:
- If the primary server goes down, a secondary server is automatically elected and takes its place (automatic failover for data center security).
- Any node can become the primary node.
- The primary gets elected through a consensus.
- The primary node accepts all the write operations.
- Secondary instances can support read operations if necessary.
- Automatic recovery.
A Developer’s Tutorial to MongoDB Replication
Now we understand the importance of data replication, let’s see how easily we can implement it with MongoDB:
Step 1: Starting the database instances
First, set up a primary server and secondary databases to replicate the data. To do so, you have to specify the path to your MongoDB installation when starting the mongod instance.
$ mongod --port 27017 --dbpath <path> --replSet <replica set name>
If the path is not specified, MongoDB will use port 27017 as the default port, but make sure to specify the port to avoid conflicts. The parameter –replSet in the above command specifies the replica set name.
Step 2: Setting up and configuring the instances of the replica set
Replicas must recognize each other’s IP addresses and host names to enable smooth communication. For instance, if you use three instances, log in to the three machines and update each node’s /etc/hosts file with the necessary private IP addresses.
154.10.33.11 mongo-node1
154.10.33.12 mongo-node2
154.10.33.13 mongo-node3
You can name instances according to your preference. Update each node’s configuration file by adding the IP addresses and the replica set name.
Step 3: Initialization
Once all the configurations are complete, you can initialize the replication process with Mongo Shell. For this, open the shell with your primary instance and then use the below command.
rs.initiate()
Upon successful execution, your system will display an output with the MongoDB version and confirm the replication commencement. Consequently, the Mongo Shell prompt will now display the name of your replica set.
Step 4: Adding more instances to the replica set
You can easily accomplish this by providing the instance name and the accurate port to the below command in the shell.
rs.add('<instance name>:<port>')
You should receive an output starting with “ok” : 1 confirming the instance has been successfully added.
Step 5: Removing instances from the replica set
Similar to adding new instances, you can also remove instances from the replica set. For this, you should start by shutting down the server.
db.shutdownServer()
Then, use the below command to remove that particular instance from the replica set once you connect back to the primary server. This operation should be performed cautiously, especially in a production environment.
rs.remove("<instance name>")
Step 6: Confirming the replica set status
If you need to check the stats of the replication set, there is a simple command you can use.
rs.status()
This command will display your replica set’s essential details and highlights, including its member instances (both primary and secondary) and their statuses.
In addition, you can use the command rs.conf() to view the configuration details of the replica set.
Step 7: Primary instance and voting
You can use the rs.status() command to check the status of the replica set, where the primary or secondary status of the member states can be seen under the parameter “stateStr“.
A replica set can have up to only seven voting members. These voting members are responsible for electing a primary node if the current primary instance fails. When there are more than seven instances in a replica set, the remaining instances should be non-voting members. You can find more on MongoDB voting here.
Boost the Resilience of Your Database
MongoDB replication plays a significant role in data availability and fault tolerance. MongoDB replica set protects data from unforeseen setbacks, such as hardware malfunctions, and refines and accelerates the data read processes. Yet, this process is only a part of a broader and more intricate data management and security strategy.
To boost the resilience of your database even further, you can employ Spectral’s AI-backed data loss prevention software. It has over 2000 detectors to discover and classify your data silos and uncover data breaches before they happen.
Get started with a free trial.