Top 9 Vendor Risk Management Software for Infosec Pros in 2023
No single organization can master all trades, which is why their success hinges heavily on their vendors. And if vendors are crucial for your business operations,
At Spectral, we’ve created the Developer Experience Manifesto which describes a gist of years of our experience building developer tools and infrastructure. It also serves as the set of core values, for us to work with and help move more effectively when we have a dilemma, a decision to take, or a trade off to perform.
This is a first post in a series that breaks down the Developer Experience Manifesto principles into case studies, and hopefully, will help you understand how to build amazing developer experience and developer tools.

Apply UX response time principles to DX
Don’t hold up developer services
Remember that you might participate in a feedback cycle
If you can’t make it responsive, make it feel responsive
Being responsive, to a large part is about being mindful of the importance of speed. We’ll discuss a very recent, and widely familiar example of why speed matters.
Javascript bundlers were largely used to build CommonJS files in the browser, by figuring out dependencies between node modules, packaging these with varying levels of sophistication to be served on a vanilla browser.
The sophisticated parts included minifying, shimming (injecting APIs that old browsers don’t support), and much later, tree shaking (figuring out which parts of a tree are actually used). A generic task of any bundler, is to also figure out dependencies as a tree (or graph), identifying conflicts, compatibility and redundancy.

Until Webpack came along, there were various milestones around bundling Javascript code for browsers. Browserify was one.
Webpack was an evolution over Browserify, in which it presented a system of concepts, that made it as the go-to bundler of the time, and it still is largely dominating.
The concepts were a flexible system of loaders and plugins: any content that you require might belong in a certain class, and its the job of the bundler to figure it out and use the correct loader for it in a modular way. Webpack also supported hot module replacement and made it widely popular.
Today, we fast forward to esbuild, which is a from-scratch rewrite of a Javascript compiler (more precisely, a bundler, but let’s go with compiler for now).
It feels like “just” a performance improvement over Webpack, on the expense of a few features that don’t exist to make the job of building it less complex.
The improvement, all in all, is a 100x improvement. Is it just a time saver?
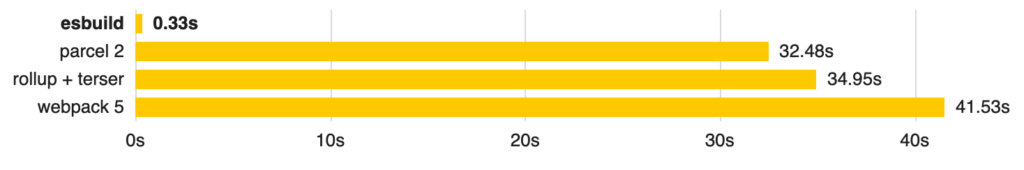
Actually, it’s more than just a time saver. A 100x improvement was enough to power a new and different approach around bundling, with tools like vite and snowpack. Even Webpack itself can be boosted up with an esbuild loader.
The thinking around building Javascript now evolved into:
And so, we’re seeing projects that are now being built (bundled) with esbuild and in parallel, type checked with tsc (for Typescript, just as an example).
Speed made esbuild loveable, so that people went through the bother of separating their workflow into two, and to “pay” for the extra complexity of that.


For esbuild it meant going to build a part of the Javascript ecosystem, out of that ecosystem: no ready to use parsers, no plugins or compilation tools to reuse, and so on.
In addition, because Go is still garbage collected, there was a careful attention given to allocations and optimization of compilation passes.
And other than that, just a massive, massive undertaking of building such a compiler (a bundler really), for a modern programming language (actually a set of languages).
Is it always correct to go with a statically compiled language when you need speed? Well, no. If you can box your requirements into the right fit for Nodejs, for example, then you’re good to go.
Here are some pointers around getting speed in interpreted languages:

No single organization can master all trades, which is why their success hinges heavily on their vendors. And if vendors are crucial for your business operations,

Integration is an indispensable aspect of modern software development. As software applications become more complex and interconnected, every component must work seamlessly together like a game

Modern companies are rapidly adopting cloud applications and services due to scalability, cost savings, and faster time to market. DevOps teams and developers must deliver fast,